Original shui bo Dan mo du chi huo Xiao dui





Tomb-Sweeping Day can’t eat Youth League.
May be the last straw to crush Shanghainese.
Don’t be afraid, the "Youth League Takeaway List+Evaluation" is coming.
Foreign brands actually faintly beat local brands?
I also found the pearl that was missed in the evaluation in previous years!
/
It is divided into four parts.
There are 14 brands, 27 flavors and 78 youth groups.
Time-honored brand, online celebrity style, foreign group and rollover group.
At the end of the article, the "Full Version of Shanghai Youth League Takeaway List" is attached.
Express delivery at the destination & you can buy it without stopping the takeaway.
●
VOL.01
Time-honored brand with stable development
Every year, time-honored brands and local time-honored stores are as stable as Mount Tai, so there are not too many evaluations.
In short, just looking for one is fresh and fresh, and you will never step on the thunder.
Pay attention to eating on the same day, the taste is better.
1. The king of cost performance in the Youth League

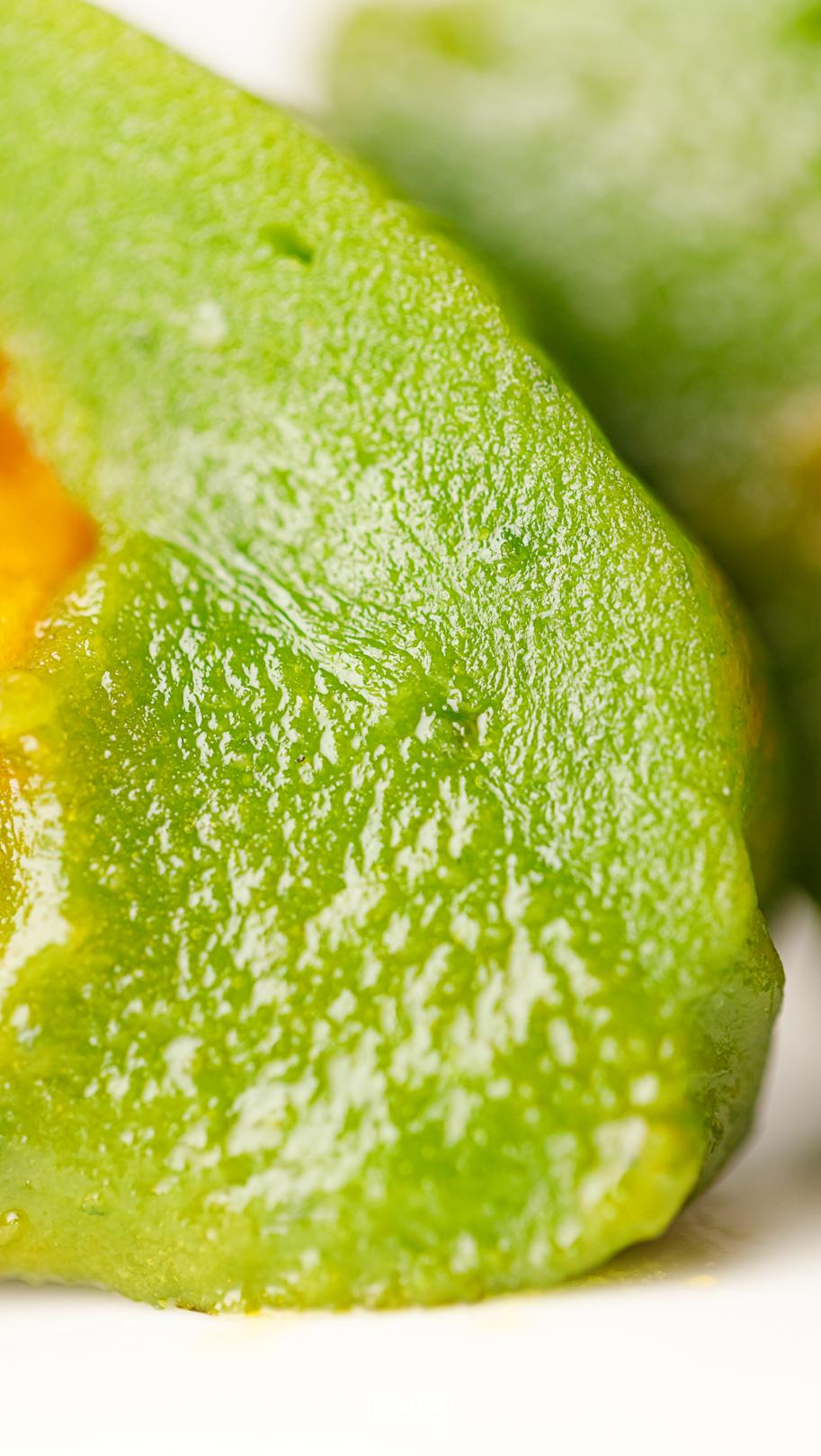
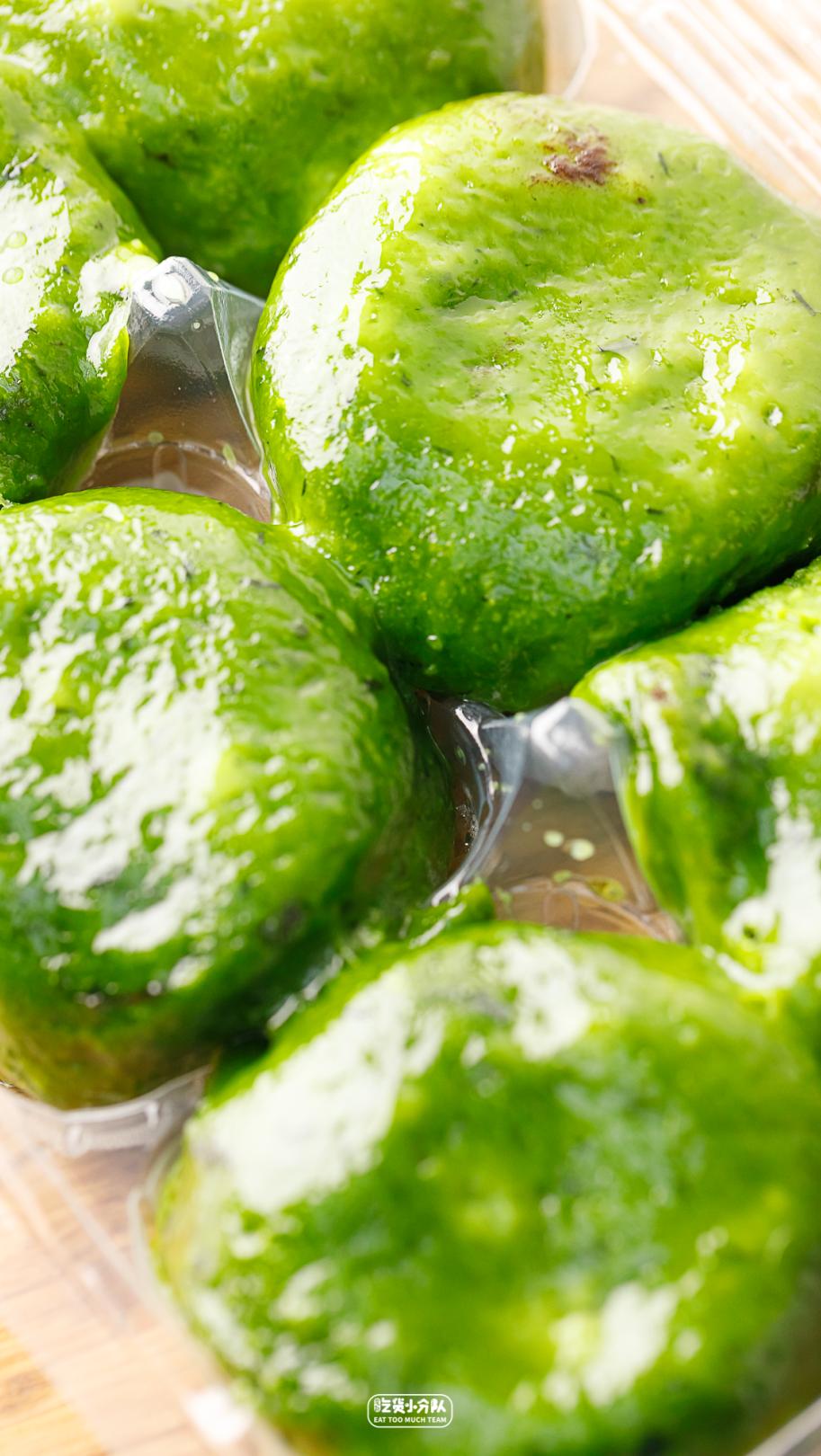
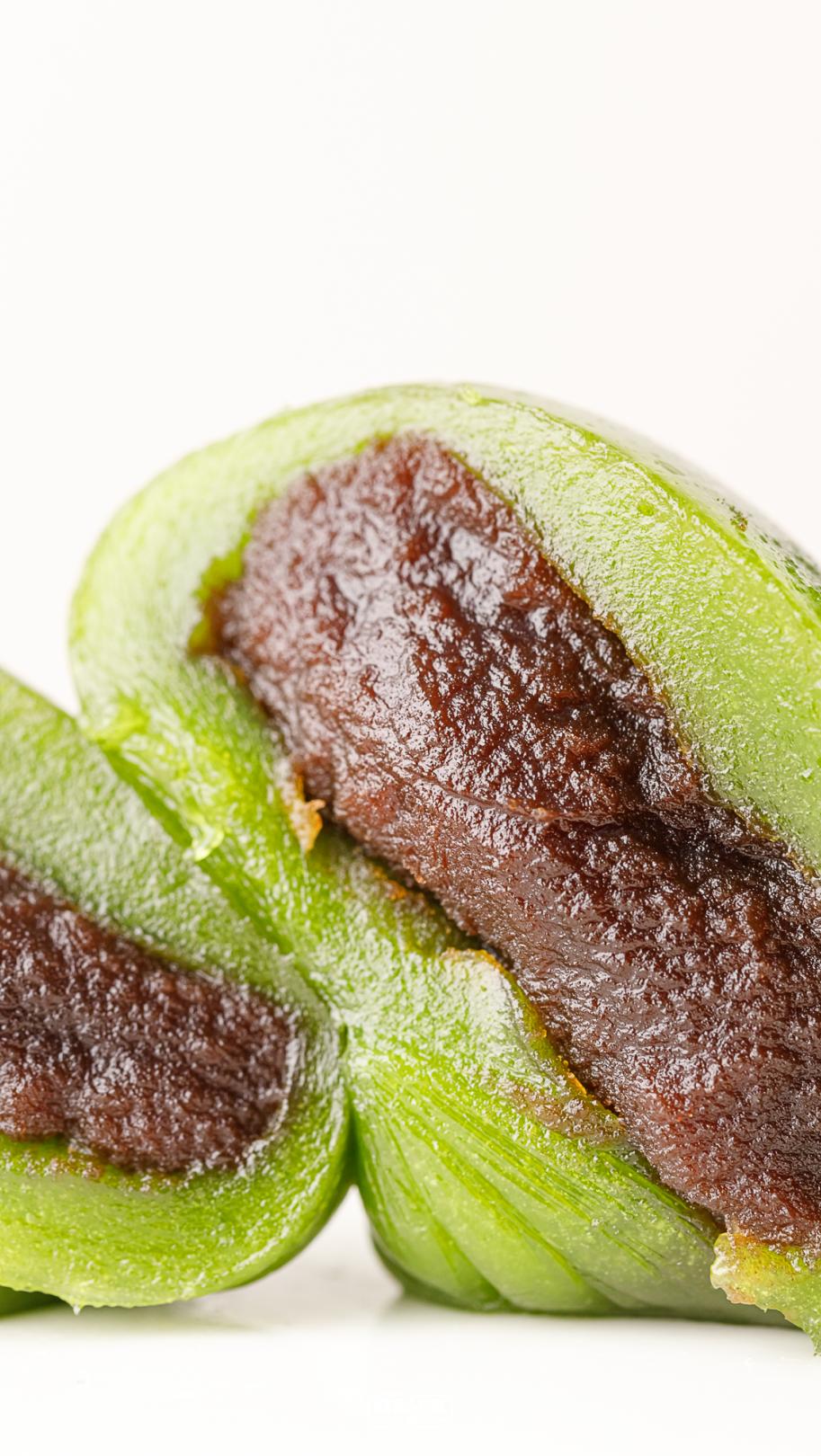
Pan yongxing cake yolk meat floss, fine sand
Skin look and feel: very thin, green color, single package.
Skin taste: it is also very sticky at room temperature.
Filling fullness: full
Overall sweetness: 5.5 points
Overall delicacy: 10 points
Cost-effective ratio: wheat green bean paste green group 4 yuan/wormwood egg yolk meat floss green group 8 yuan/only.
takeaway
Meituan (Jing ‘an, Huangpu)
* backstage reply keyword "Youth League" to see the full version.
evaluate
The surprising online celebrity pastry shop has a high cost performance and a dark horse taste.
The skin is thin and stuffed, and the skin is moist and sticky.
Eating in the mouth will not choke the throat, and it will not harden at room temperature.
No one was detected in the previous evaluations.
Wheat green bean paste green ball

The whole youth league is propped up by stuffing! The bean paste stuffing is delicious, with a unique sweet-scented osmanthus fragrance and a strong flavor. Many people think that the taste of green dough skin is too bitter, and they seriously suspect that they didn’t buy it right. The well-made green dough is faint plant fragrance and rice fragrance. We’re a little too hot for this one, but even if it’s not heated, it’s soft and sticky, even more sticky than my boyfriend!
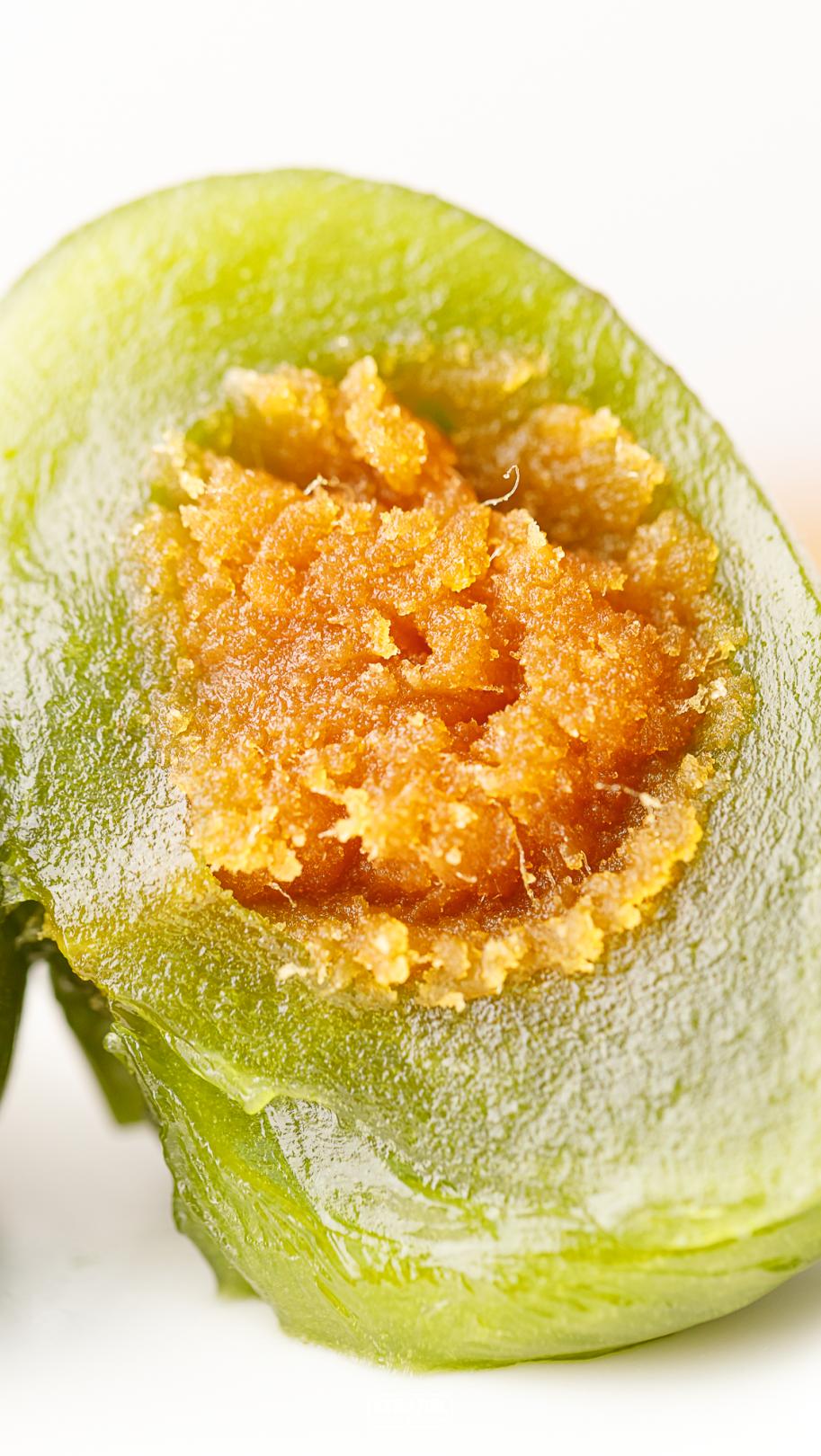
Wormwood egg yolk meat floss green ball
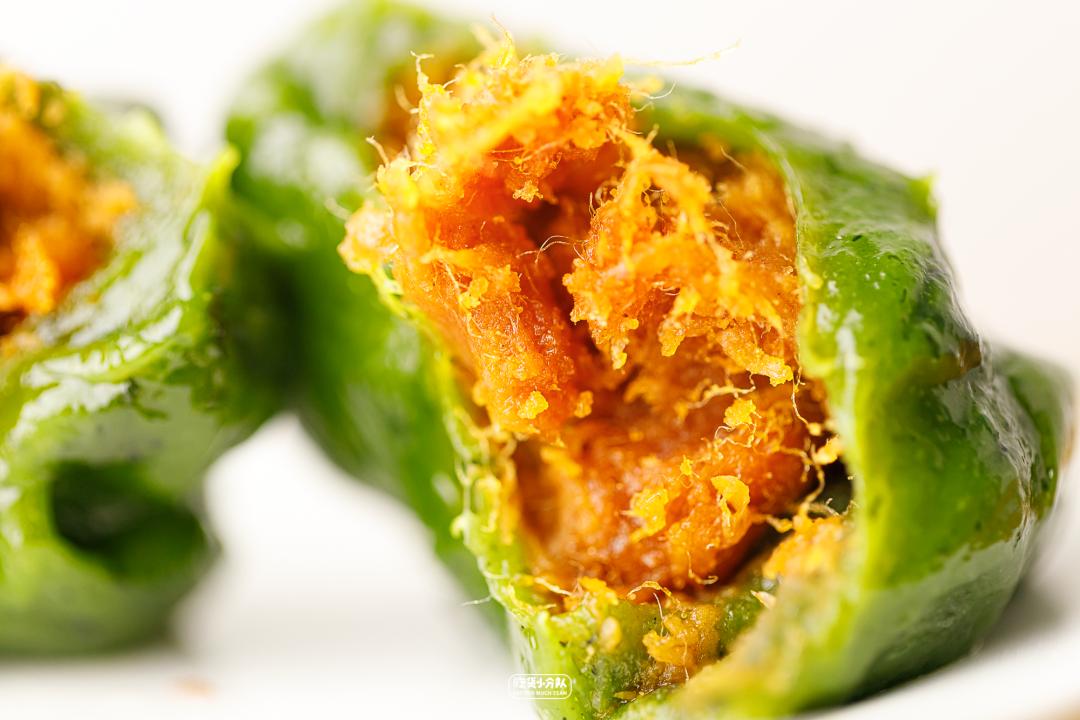

Eating stuffing alone will not be salty, and there will be no complicated seasoning. The stuffing in the middle is also explosive, and the amount given is particularly large. It is clear and chewy. The invagination is slightly oily and tastes better. The most traditional wormwood turf is slightly more herbal than wheat green husk in theory, but it tastes little different in practice.
2. The most recommended time-honored brand with fluffy egg yolk.

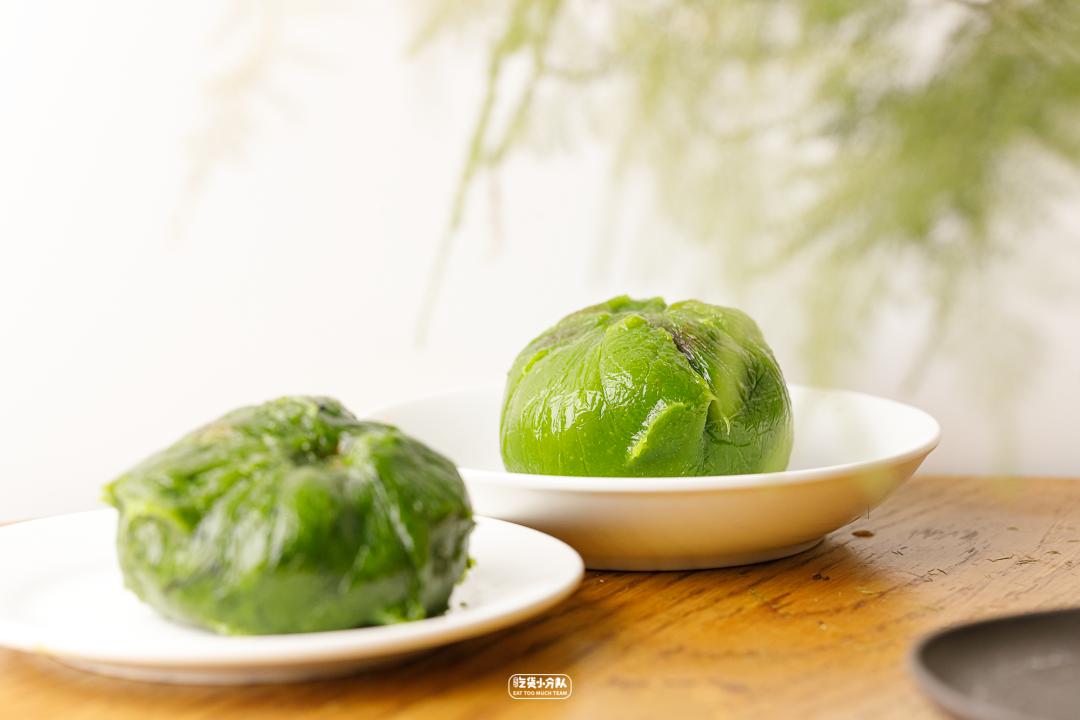
Hongkou cake balls with egg yolk, meat floss and bean paste
Skin look and feel: large, oily and smooth, and the granules are packaged separately for easy storage.
Skin taste: not sweet, wormwood fragrance.
Filling fullness: fullness
Overall sweetness: 5 points
Overall delicacy: 10 points
Cost-effective ratio: 5.9 yuan with bean paste flavor/only 100g.
Salted egg yolk tastes 10.5 yuan/100g only.
takeaway
Meituan (Quanchengsong)
* backstage reply keyword "Youth League" to see the full version.
evaluate
Time-honored brands with daily sales of over 10,000 only sell two traditional flavors.
The front shop and the back factory are all freshly baked.
The skin is made of raw powder, and the taste is more q-elastic.
It belongs to the old brand that can stay a little longer, and it can stay for 3 days in cold storage.
Egg yolk floss
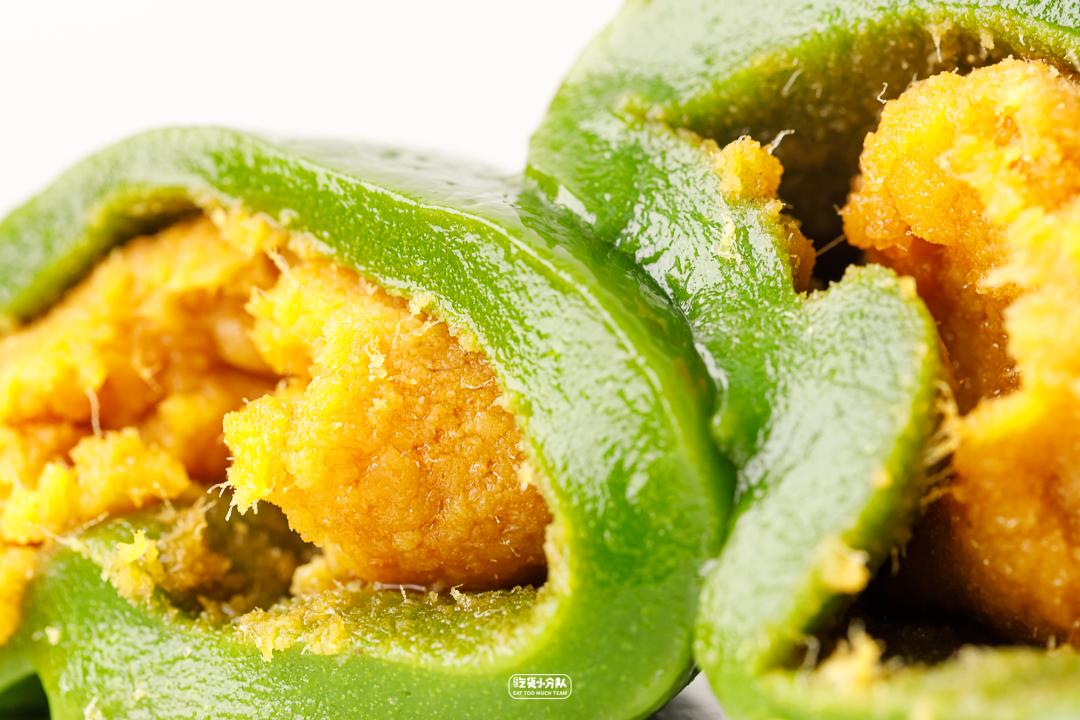


The stuffing is very full, the egg yolk floss is the most delicate and soft this time, and the salty taste is also the lightest this time, and there is no egg smell at all (although the fragrance is still not as good as Wuxi Xiaohong Cake Group). After eating a circle, the most surprising smell of salted egg yolk is it. Take a big bite, and you can eat thick stuffing in every bite, and your satisfaction is bursting.
bean paste

The skin won’t harden at room temperature, and its water retention is good. After drying for one day and heating, it immediately returns to sticky and sticky. Although it is very brushed and soft, it doesn’t stick to the mouth at the entrance, and it tastes full of elegant plant aroma. Concealed in soft sand, full of bean fragrance.
3. The most recommended time-honored snacks
-Explosicum Matcha Group

Shen Dacheng Matcha Milk Group and Matcha Durian Group.
Skin look and feel: there is a layer of powder that does not stick to hands and feels soft.
Skin taste: not sweet, very soft.
Filling fullness: fullness
Overall sweetness: 4-4.5 points
Overall delicacy: 10 points
Cost-effective ratio: Matcha milk ball 29.9 yuan/box 200g
Matcha durian group 18.9 Yuan/box 100g
takeaway
Box Horse APP (covering all districts in Shanghai)
* backstage reply keyword "Youth League" to see the full version.
evaluate
Shen Dacheng, with a history of 140 years, is a big cow in the youth league, playing with various tastes.
Making dumplings into snacks is a bit expensive, but it tastes a bit subversive.
The skin is delicate and soft, put it on the frozen layer and take it out, and it will soon thaw.
Matcha milk ball
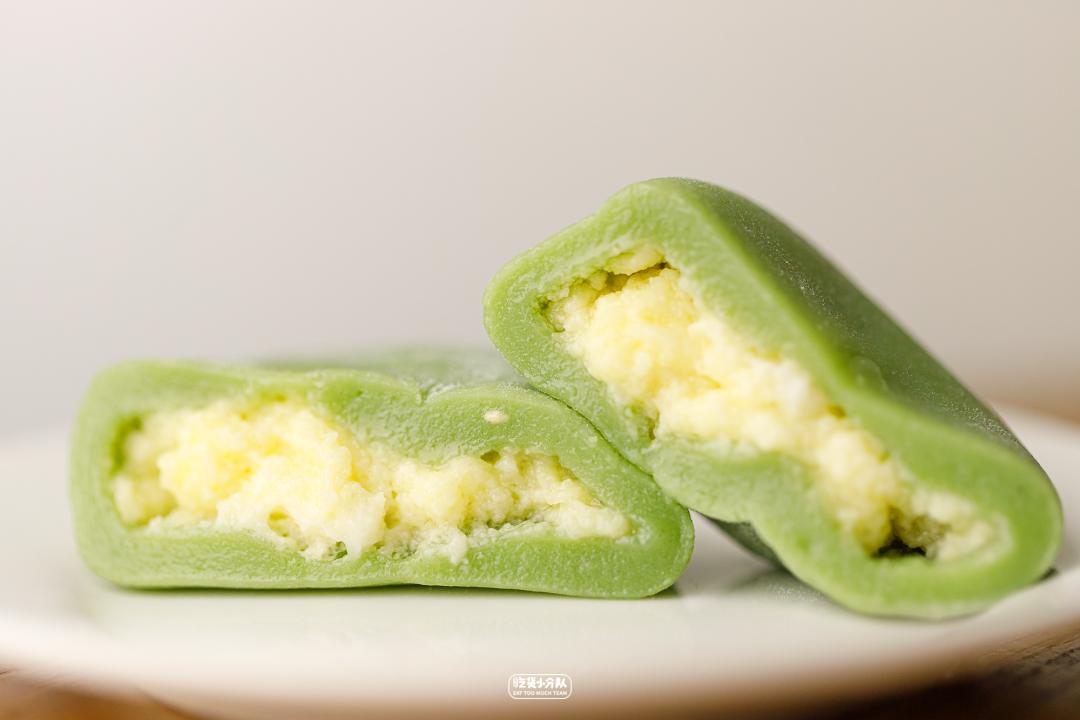


The stuffing in the middle is made of cream and solid milk, which even smells of oil when eaten. The milk is not condensed together, but like a flowing heart. The sweetness is very restrained, which is the least sweet invagination in the whole evaluation. The skin feels soft and soft, and it is malleable and elastic when pulled, which can do better than many fresh Dafu.
Matcha durian Tuan

The skin of durian balls will be a little thicker and a little harder, and the Explosicum in the middle is the taste of fresh durian, which is gently softened into the mouth. Because the invagination adds real durian pulp, which is a little sweeter than the milk ball.
4. The most recommended time-honored brand with bean paste flavor
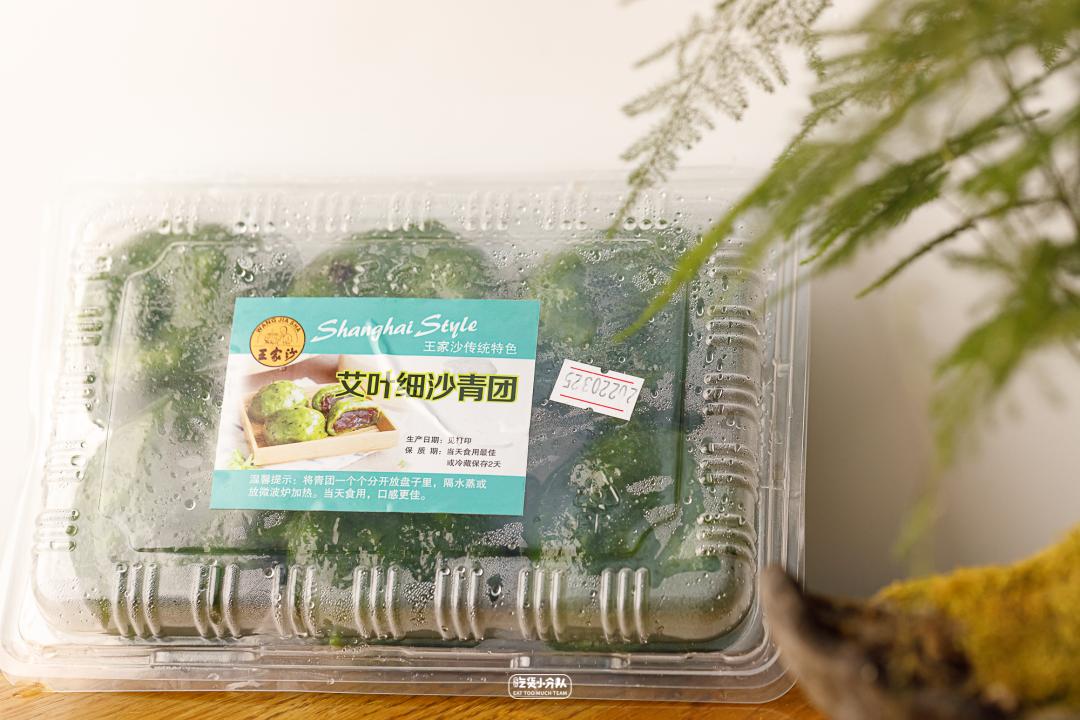

Wang Jia sha ai ye Xi sha
Skin look and feel: dark color
Skin taste: sticky, brushed, refreshing aroma.
Filling fullness: particularly full.
Overall sweetness: 5.5 points
Overall delicacy: 9.5 points
Cost performance: 41.3 yuan/6 PCs (online shopping)
takeaway
Meituan (at present, the Youth League has suspended takeout)
Can be called to run errands.
* backstage reply keyword "Youth League" to see the full version.
evaluate
An old brand founded in 1945.
Rare, the most traditional use of natural mugwort leaves, making green skin.
In last year’s Youth League evaluation, many local fans strongly urged Amway.
It’s big enough for a family to stutter for six months (joke: D).

Tearing is the fragrant bean paste, and the sweetness of the middle beans is slightly sweeter than that of Hongkou cake dough. The bean paste is ground very finely, so you can’t eat it.
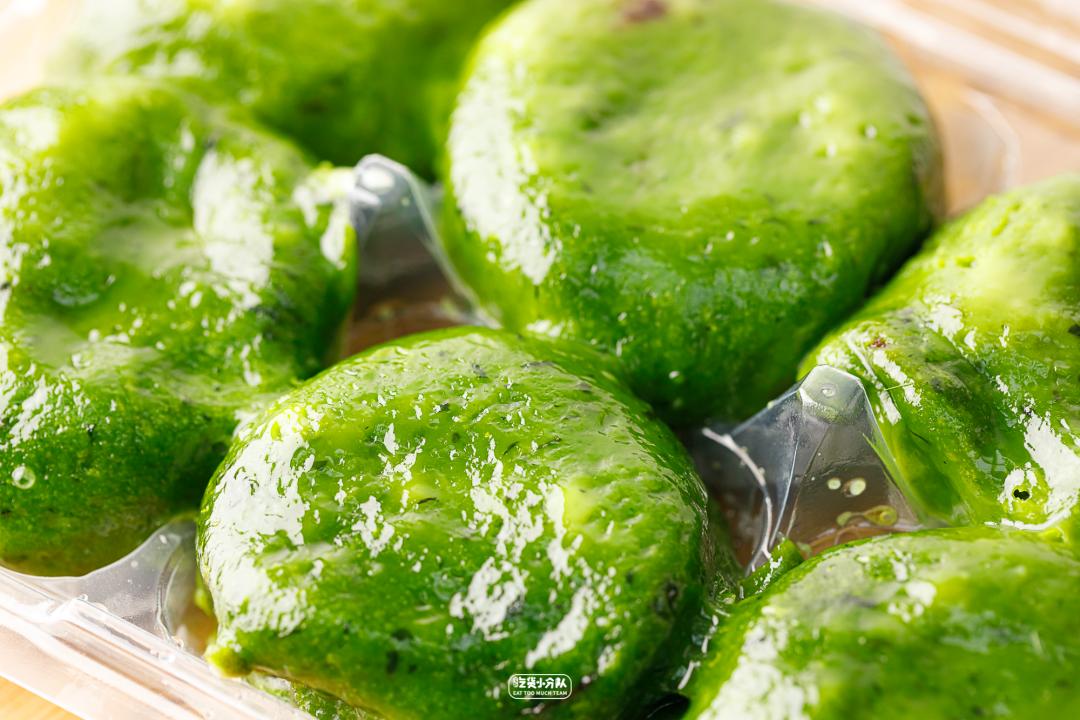
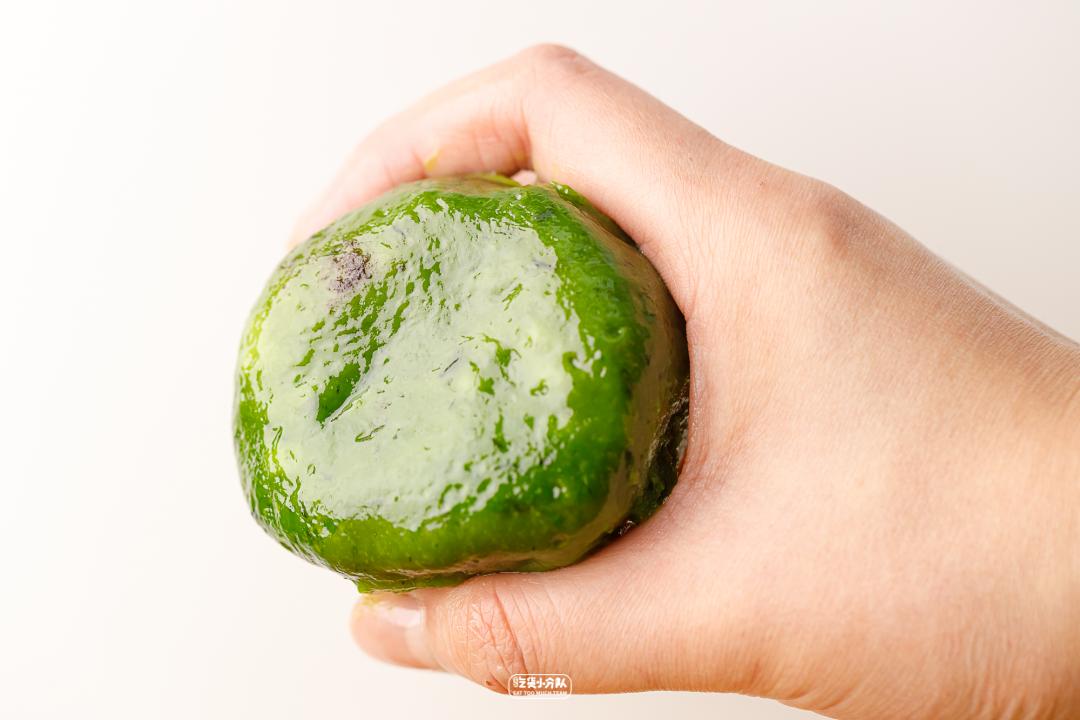


The skin is moderate in thickness, and it is a little hard to take out, but it will become particularly soft when heated casually. The aroma is very refreshing, and the more you chew, the more fragrant it is, and it is fresh and greasy, and its extensibility is particularly good. Looking for a dream group, it has to be Master Wang!
5. Sweet and sour fruit bean paste green ball

Kutokuhayashi blackberry fine sand
Appearance of skin: thin skin, a little dry (transportation reasons)
Skin taste: soft, waxy, brushed and not sweet.
Filling fullness: it’s still full.
Overall sweetness: 5 points
Overall delicacy: 9.5 points
Cost performance: 50 yuan /6 PCs.
takeaway
Meituan (Huangpu District)
* backstage reply keyword "Youth League" to see the full version.
evaluate
This year is just 100 years old.
The most famous are Malantou Youth League and shepherd’s purse Youth League.
Innovative tastes such as vegetarian crab powder green group and blackberry bean paste green group are also popular.
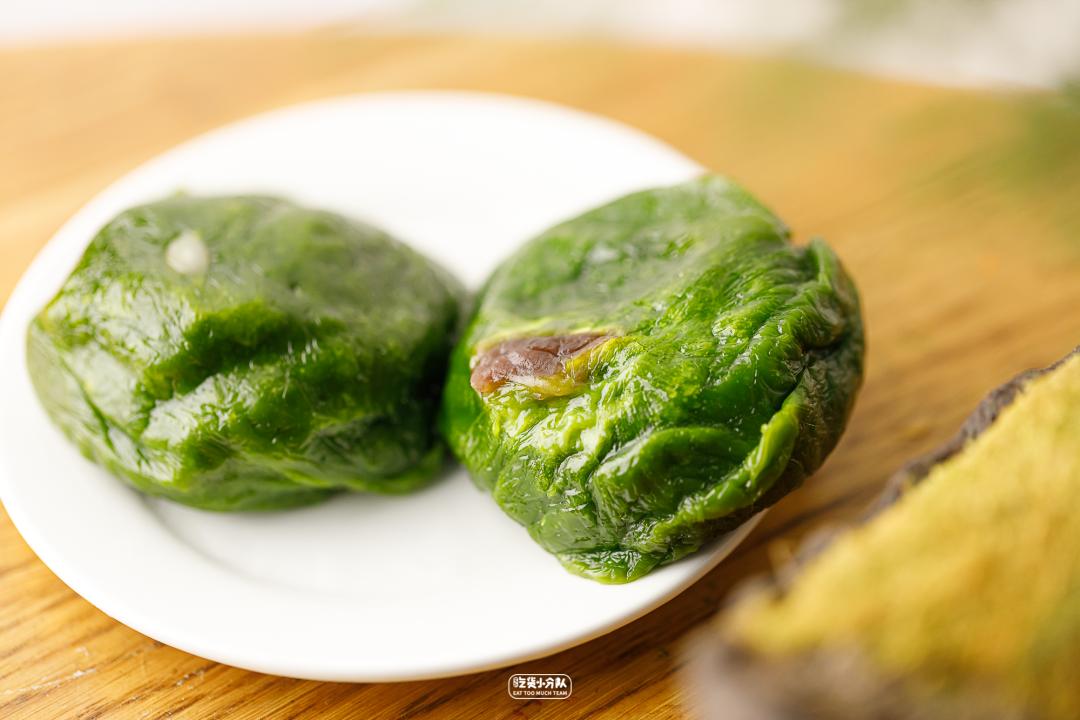

We bought it, probably because of the take-away extrusion and air leakage. It looks like a small broken ball with a little bad appearance and some skins are a little hard, so once again, we must not blow the hair. However, the flaws don’t cover up, and the taste can still be hanged.


The red bean paste is very moist and can taste the sour taste of black plum, which is sour and sweet. The stuffing is not very full, but it tastes more balanced with soft glutinous skin. The brushed green skin and the red bean paste with a flowing heart inside will blend together slightly.
6.3 colors of time-honored online celebrity Youth League
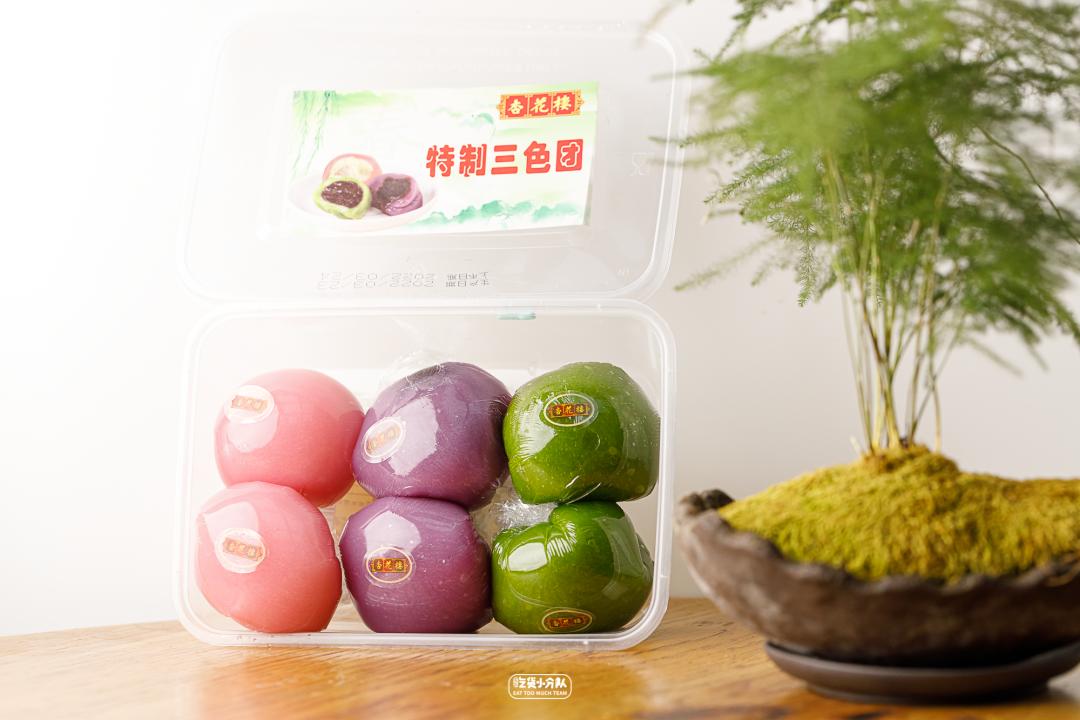

Xinghualou 3-color "Youth League"
Skin look and feel: the shape is good
Skin taste: the skin is restrained in sweetness, relatively q-elastic, and the extensibility is average.
Filling fullness: very full.
Overall sweetness: 7.5 points
Overall deliciousness: 7.5 -9 points
Cost performance: 95 yuan/box /6 PCs.
takeaway
Meituan (Quanchengsong)
* backstage reply keyword "Youth League" to see the full version.
evaluate
Founded in 1851, it stood in line for 3 hours at the height of the fire, and the price of scalpers increased tenfold.
It’s an old brand that likes innovative tastes very much.
In that year, the pink and purple "Youth League" was launched, which caused the whole network to punch in.
There are also flavors such as shredded chicken bacon and cheese beef.
Green-green ball with bean paste

Dafu in the youth league is made of glutinous rice from Wuchang, Heilongjiang. QQ is soft, not very sticky, and has a faint fragrance. But the rose bean paste is too sweet. Perhaps the signature salted egg yolk meat floss green ball is the king.
Pink-yogurt flavor
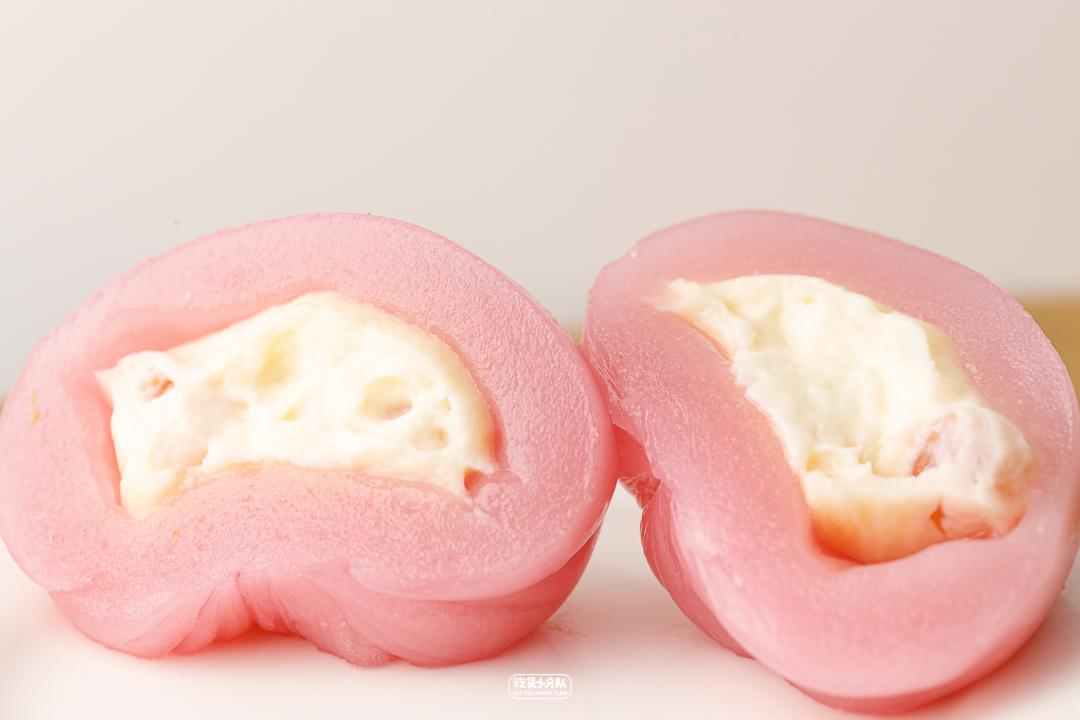
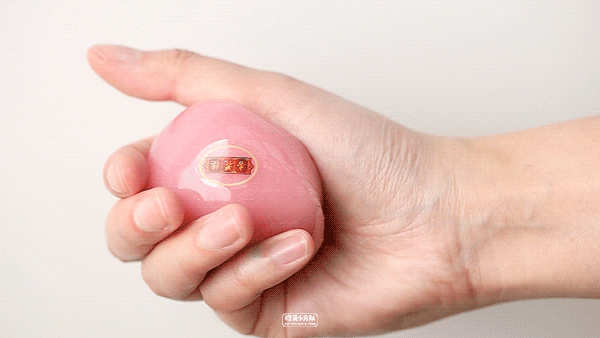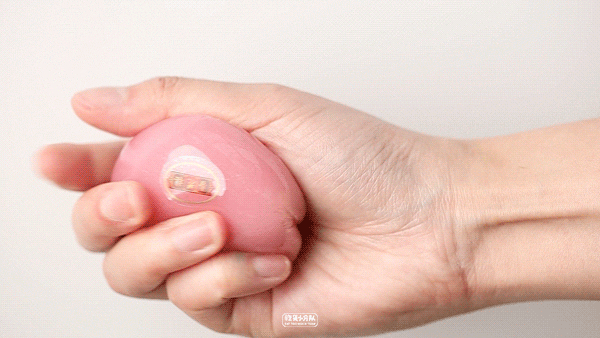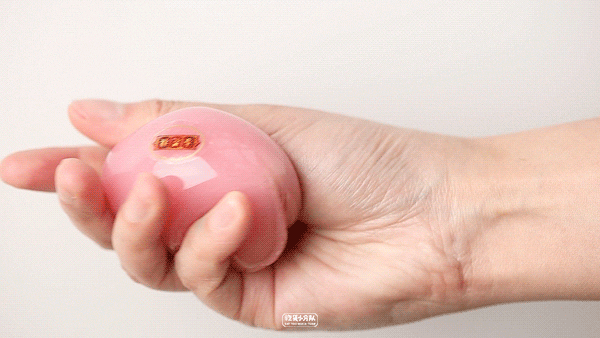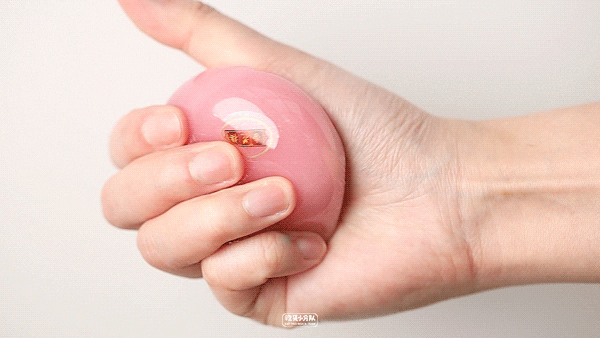

Online celebrity pink "Youth League" newly released in 19 years, there is no need to queue up to buy it this year. Thick cheese flavor, the overall milk flavor is quite sufficient, and you can also eat coconut fruit, and the sweetness will not be too exaggerated. This one is most recommended.
Purple-purple sweet potato and bean paste flavor
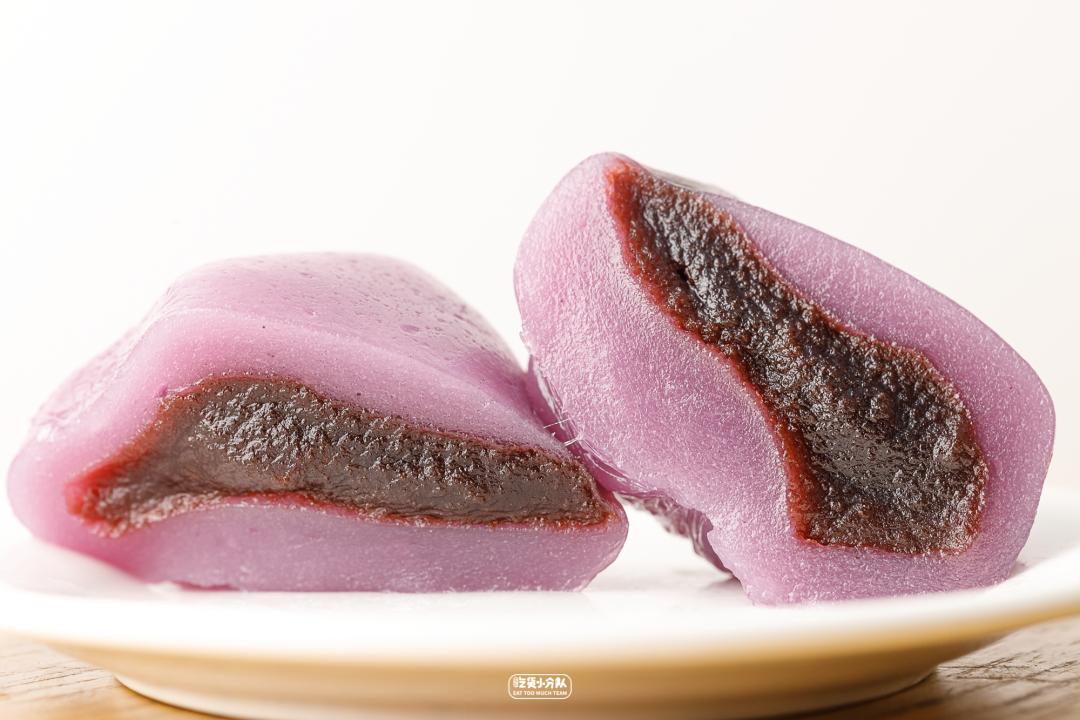

It is a online celebrity flavor produced in 19 years, with sweet bean paste in the middle, fine bean paste and a faint rose flavor.
●
VOL.02
Online celebrity & Wonderful Youth League
It’s not a youth league that is selling now, but it always seems a little less interesting.
Many of them have also left the category of youth league.
Run to the avenue of Dafu, snacks and other cakes.
Either because it is original and delicious, or because it can be preserved for a long time.
It’s still worth a taste
1. Edible "blush" dumplings
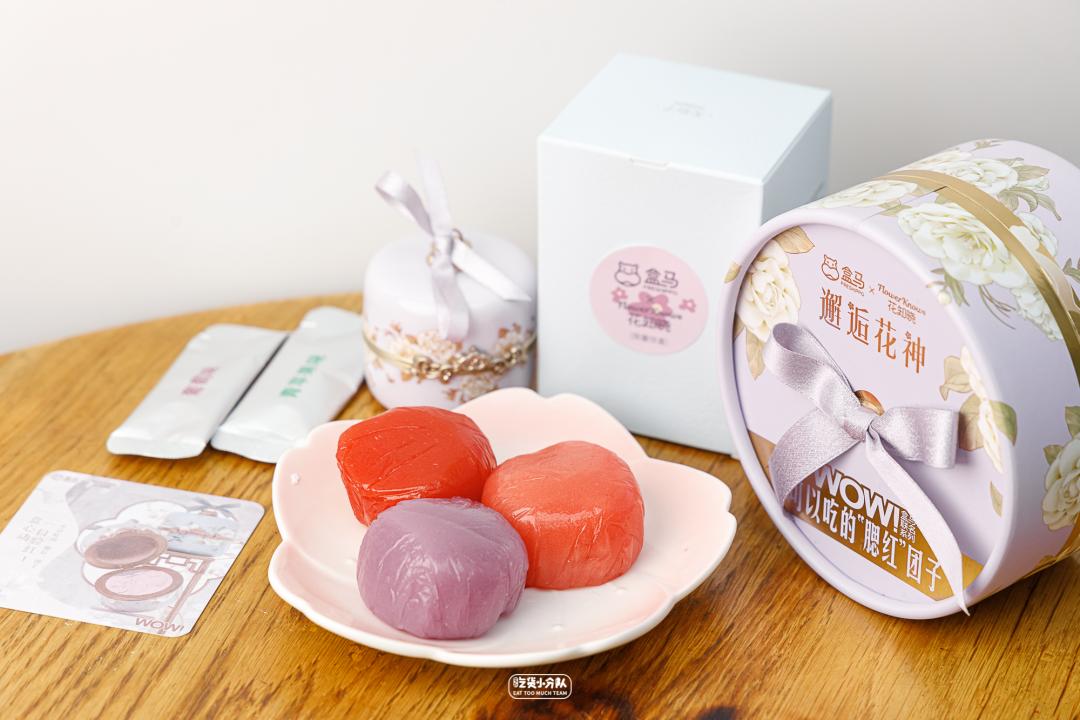

Box horse x flowers know WOW meets the flower god "blush" dumplings
Skin look and feel: pink blush color, mini head.
Skin taste: more Q-bomb, with different tastes, sweeter.
Filling fullness: relatively full.
Overall sweetness: 9.5 points
Overall deliciousness: 6.5-7 points
Cost performance: 35.9 yuan/box 190g
takeaway
Box Horse APP (covering all districts in Shanghai)
* backstage reply keyword "Youth League" to see the full version.
evaluate
Co-branded with beauty makeup, nice blush color scheme.
People want to ask about the color number. The packaging is also exquisite, and you can collect it after eating.
Chestnut creamy taste


You can eat a piece of chestnut granules, and the taste of chestnuts is relatively cured. When eating, it can be served with two flavors of pop rocks, and the feeling of bouncing with your mouth is quite exciting.
Taotao cheese flavor
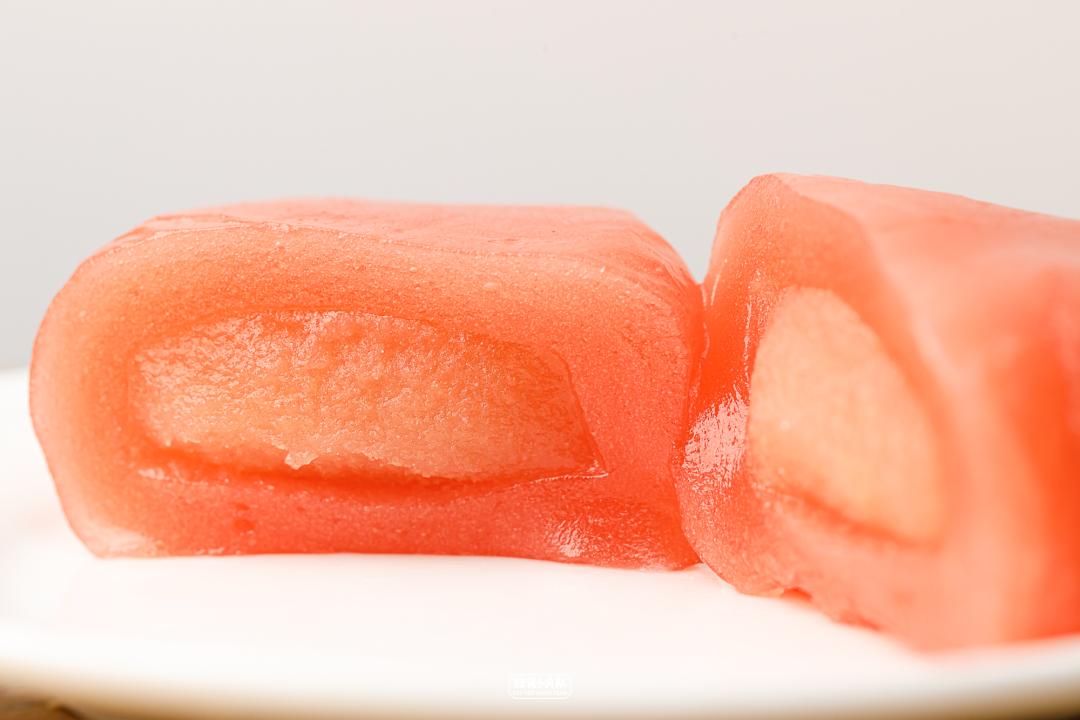

Overall, it has a strong cheese and peach flavor. Just smelling it, Momoka is quite obvious. The outer skin QQ is different from the traditional youth league. The invagination tastes like Cantonese moon cakes, which are sweeter.
Taro milk flavor
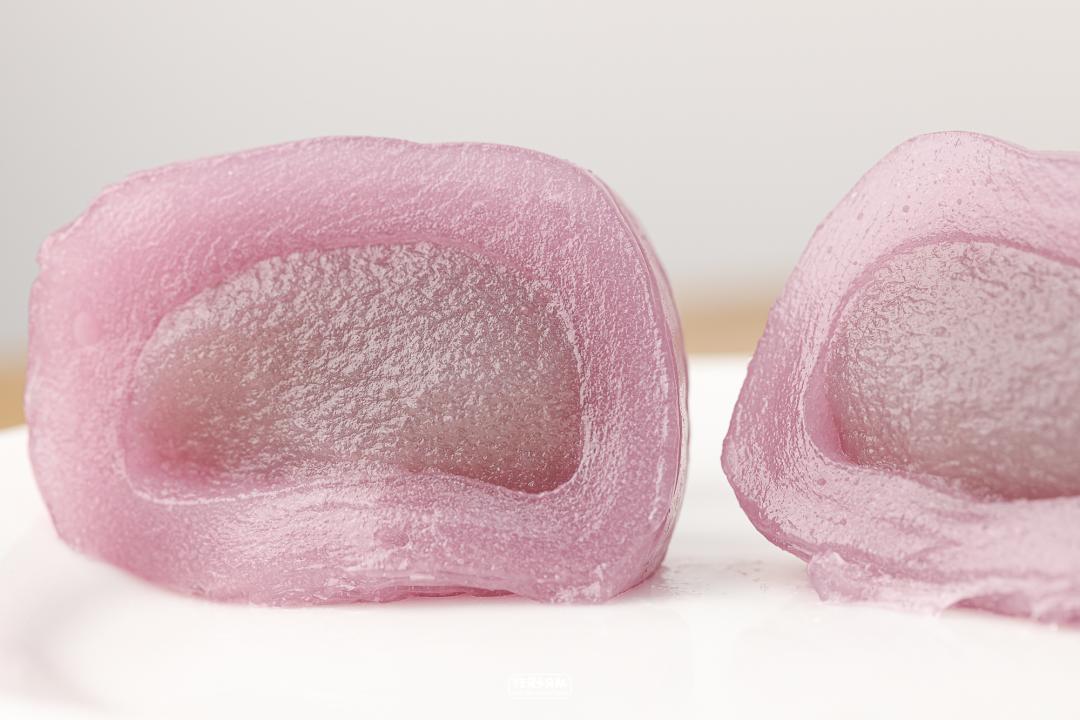
The sweetest of the three models, each of which tastes like drinking milk tea, is suitable for the dessert party.
2. Stripes of youth league

Box horse x tiger head bureau egg yolk seaweed meat floss green ball cake
Skin impression: the green ball is made into a "strip cake"
Skin taste: light taste and good extensibility.
Filling fullness: very full
Overall taste: soft and glutinous
Overall sweetness: 7 points
Overall delicacy: 7.5 points
Cost performance: 19.9 yuan/box 300g
takeaway
Box Horse APP (covering all districts in Shanghai)
* backstage reply keyword "Youth League" to see the full version.
evaluate
Box horse and the Chinese dim sum shop that burst into flames jointly signed, and the two chefs were ecstatic.
Super showman’s striped youth league.

The skin can be pulled and brushed at will, and it is soft to pinch. The unified feature of the green ball that can be preserved for a long time is that it is not too sticky. It seems that it is easier to eat when it is made into long strips, and the stuffing will not fall everywhere.
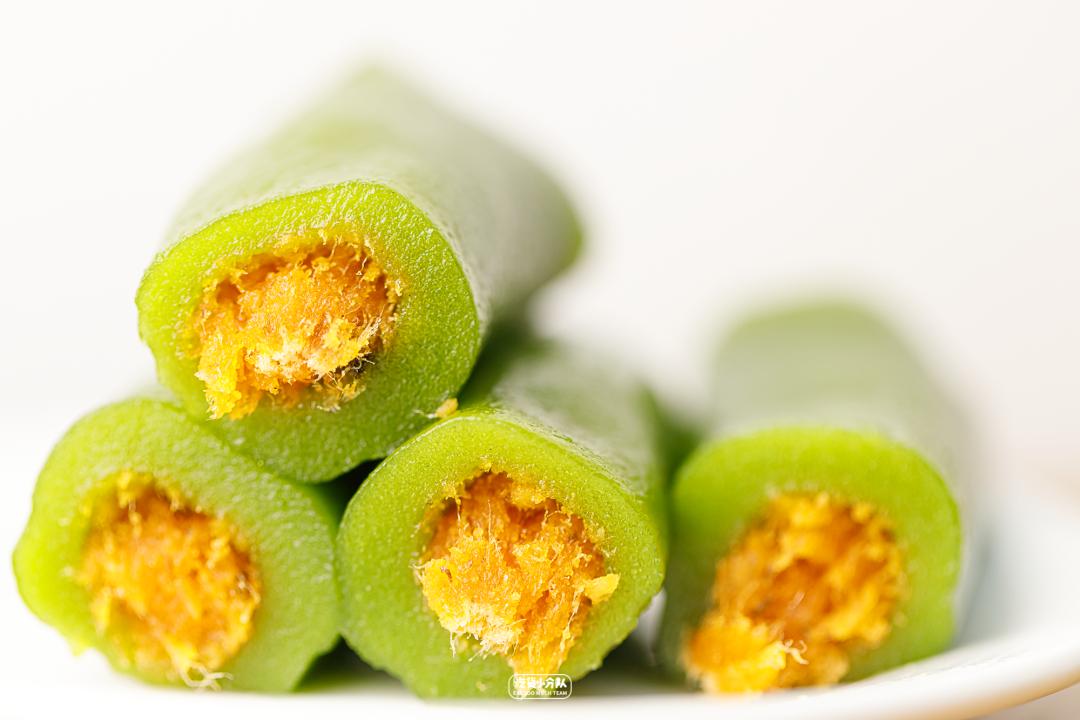

The invagination is the taste of egg yolk seaweed floss, and the ratio of invagination to skin is just right. The light skin just neutralizes the salty and sweet taste of invagination and is not too oily.
3. Hangzhou China Time-honored Brand Innovative Taste
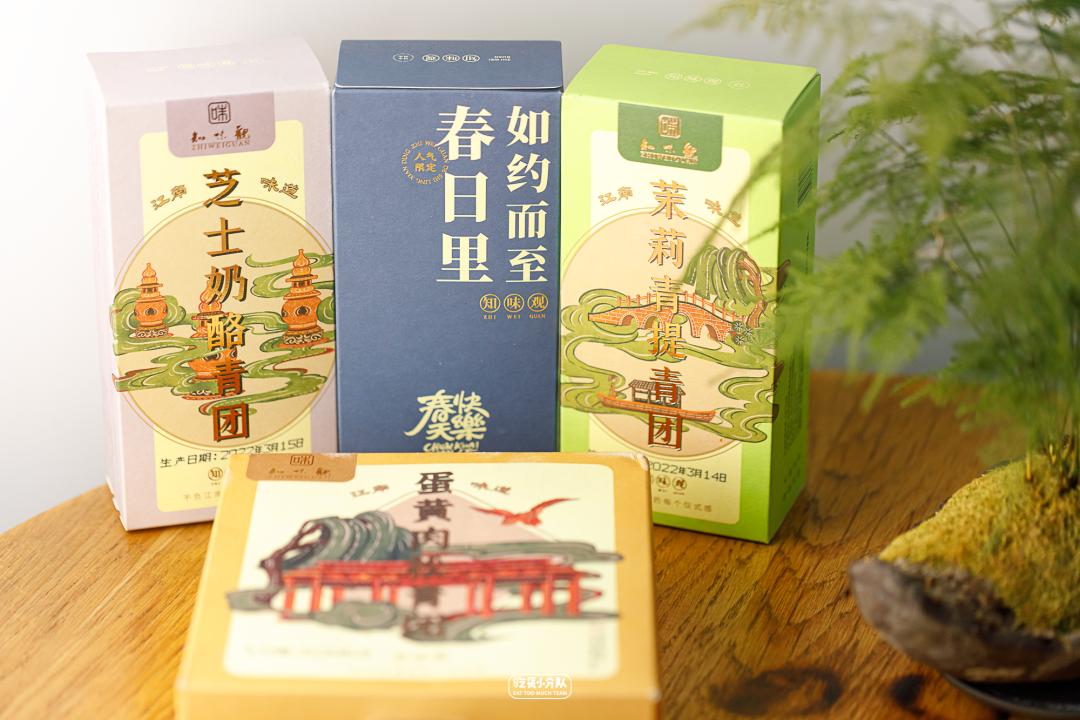

Zhiweiguan egg yolk floss cheese
Jasmine green sea salt raw coconut latte
Skin look and feel: slightly transparent, excellent extensibility.
Skin flavor: sweet, with strong green wort and wormwood flavor.
Filling fullness: fullness
Overall sweetness: 7 points
Overall deliciousness: 5 -7.5 points
Cost performance: 5.9 yuan/box /2 PCs.
takeaway
Box Horse APP (covering all districts in Shanghai)
* backstage reply keyword "Youth League" to see the full version.
evaluate
Hangzhou’s time-honored Chinese concept of knowing taste was founded in 1913.
Packaging is a very pink Chinese style.
The sweetness is relatively restrained, and it is not bad in the small snacks of the Youth League.
Egg yolk floss
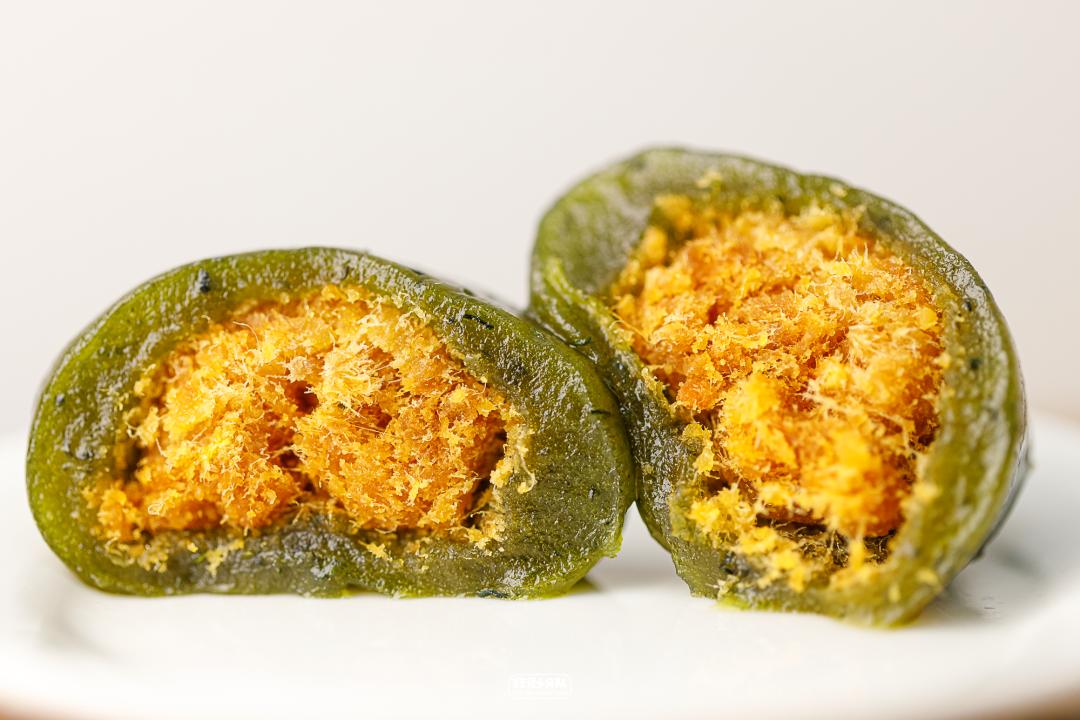

The salted egg yolk in the middle is chewy, and it is very fragrant with New Zealand butter. The key is not sweet and greasy. On the contrary, the skin is sweet, which can be 8 -9 points sweet. At room temperature, the epidermis can be drawn crazily, but it is not glutinous, but has a slightly Q taste.
Cheese, cheese.
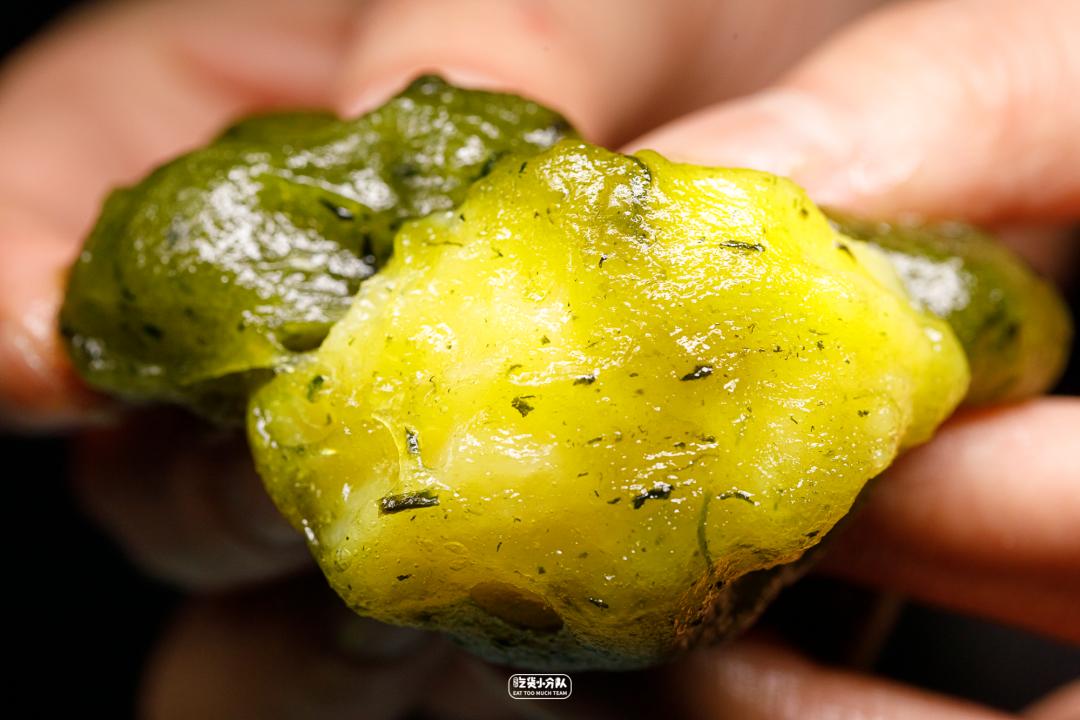

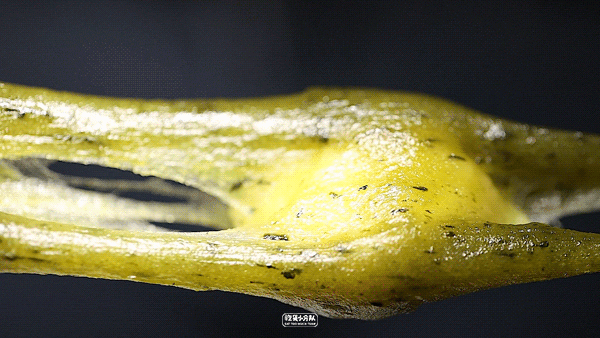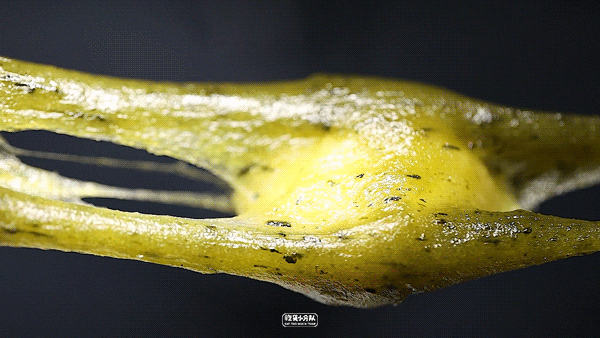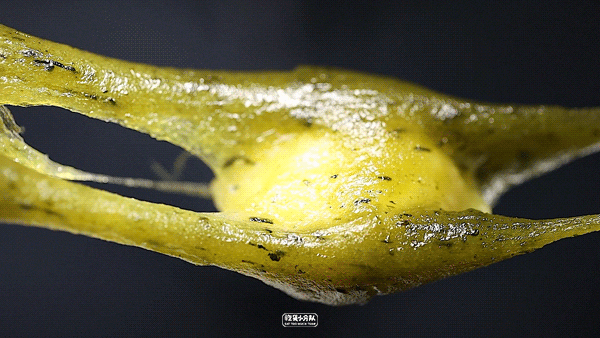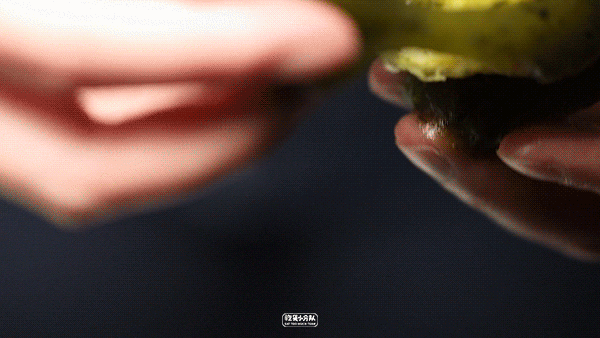
Cheese cheese sandwich, the cheese flavor is still very strong, it is hard to eat at room temperature and it is not easy to melt. After heating in the microwave oven for 30 seconds, it will soften slightly, and the skin will melt like porridge, which will be more delicious.
Jasmine qingti
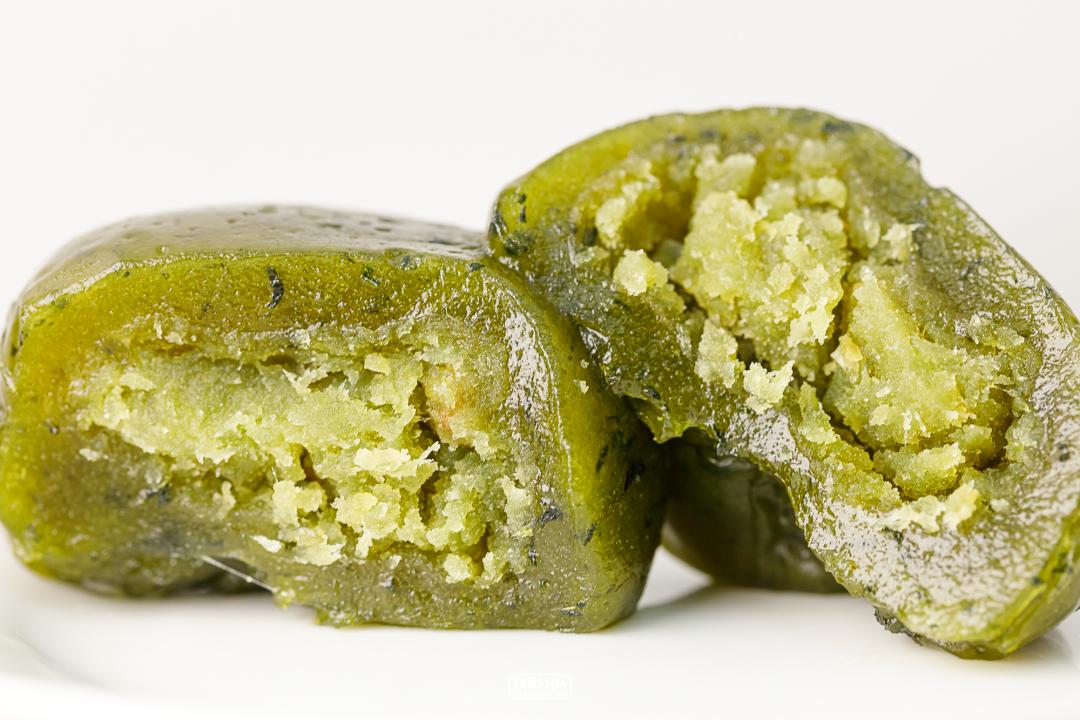

Jasmine flavor and green flavor can be smelled at once, with a faint fragrance and not too sweet.
Sea salt coconut latte
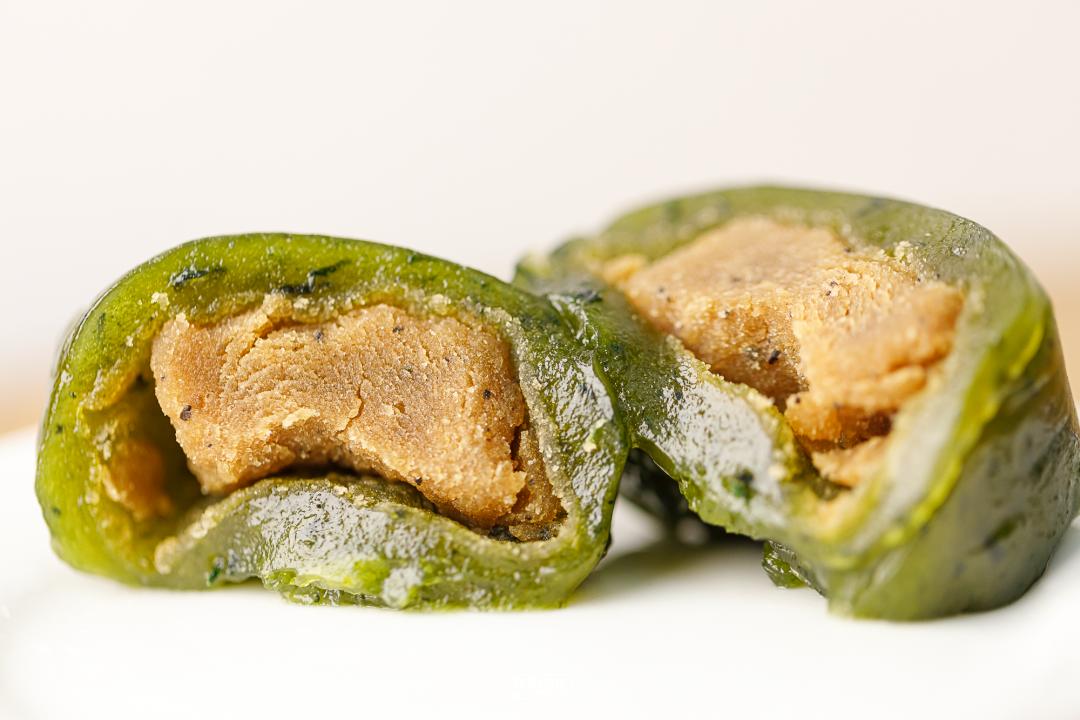


The invagination is soft, like a moon cake, and the latte is very heavy, a bit like coffee candy, slightly bitter. Personally, the stuffing tastes a little separated.
4. Minority Hakka salty tea tastes green.
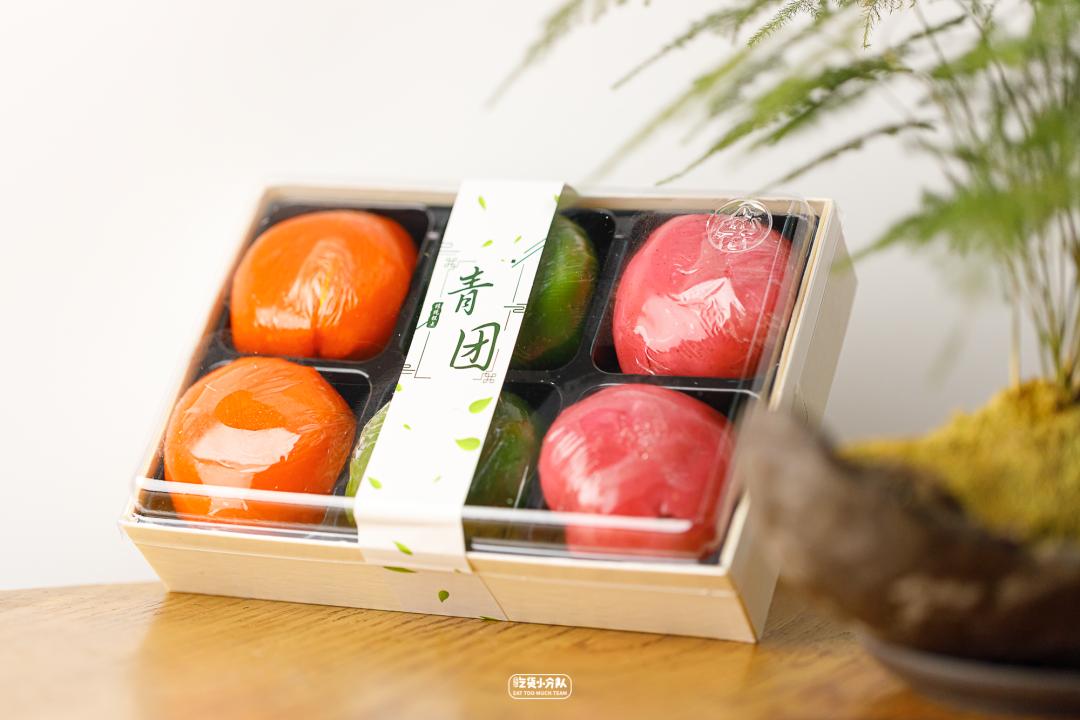


Shanhaichao salty tea cake, dried tangerine peel and bean paste, salted egg yolk meat floss
Skin look and feel: 3 colors, each round.
Filling fullness: fullness
Cost performance: 88 yuan/box /6 PCs.
(Off the shelf)
evaluate
Shunde restaurant Shan Haichao and master Lin Zhenguo, the master of Cantonese cuisine,
Together, we created a green group with salty tea flavor.
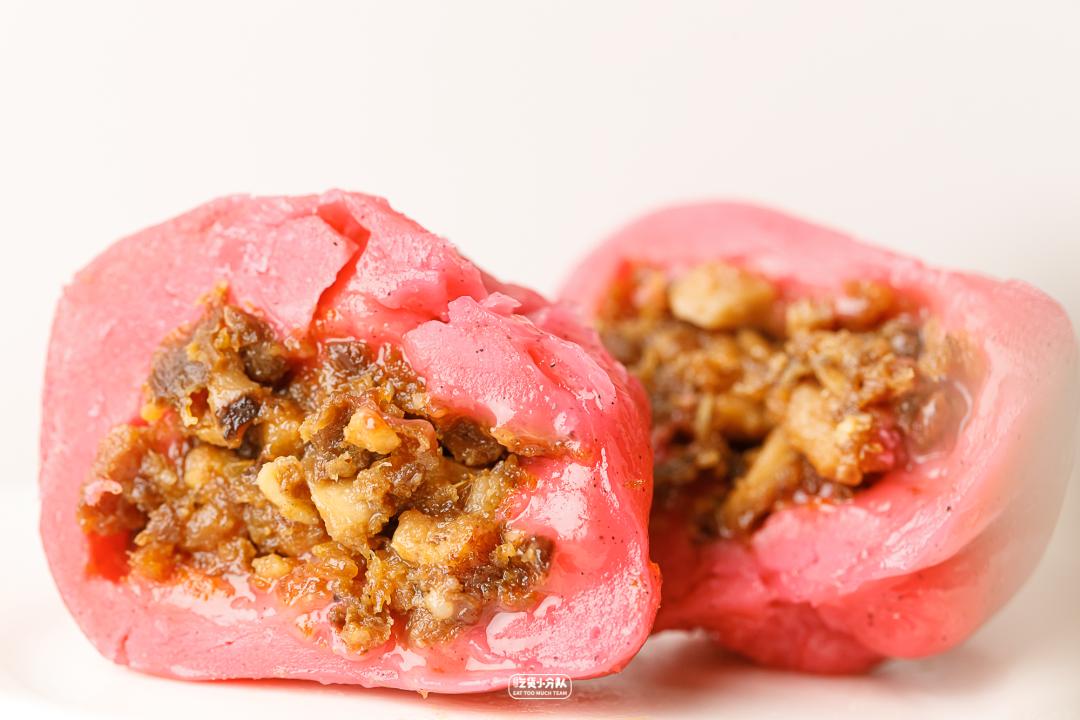

The combination of meat and vegetables in the middle, such as shrimp, mushrooms, pork and preserved vegetables, is Hakka’s taste.
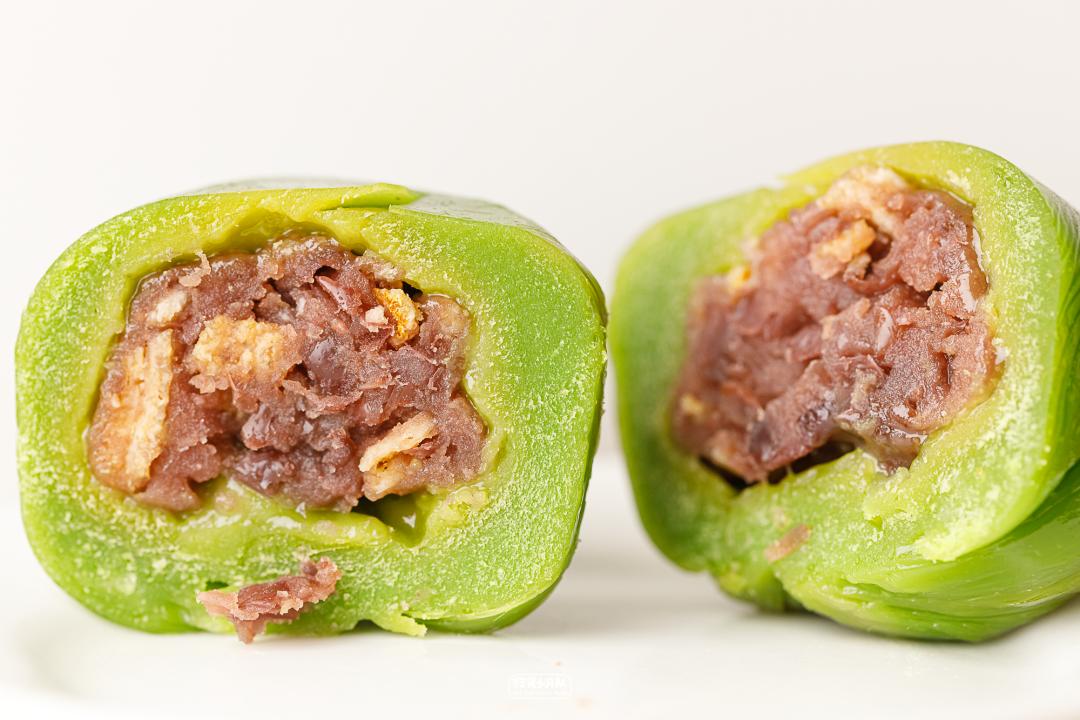


A gift box has three flavors, but it can only be stored for a few days. The package is particularly beautiful and can be given as a gift.
●
VOL.03
/
Online celebrity gaotuan branch is now selling in the field.
This time it was completely planted with grass, and both families were unexpected.
There is even a tendency to surpass Shanghai’s time-honored brands.
However, the youth league in other places is delicious, and after transportation,
All tastes should be discounted, so it’s better to eat locally.
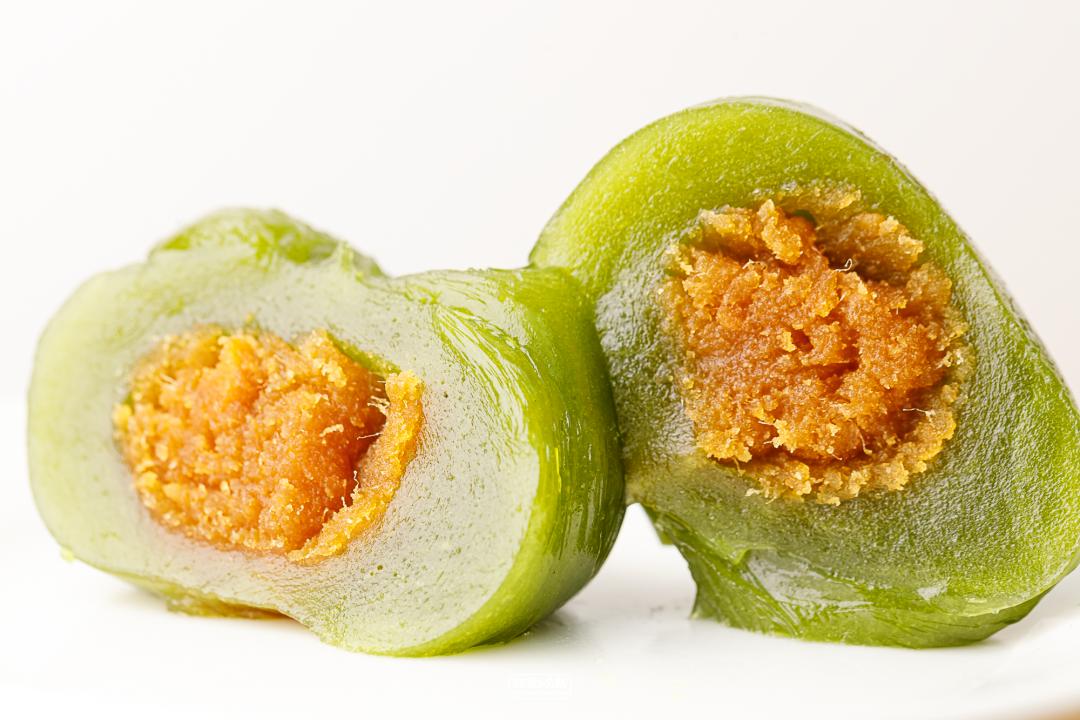
1. The most amazing invagination in the audience
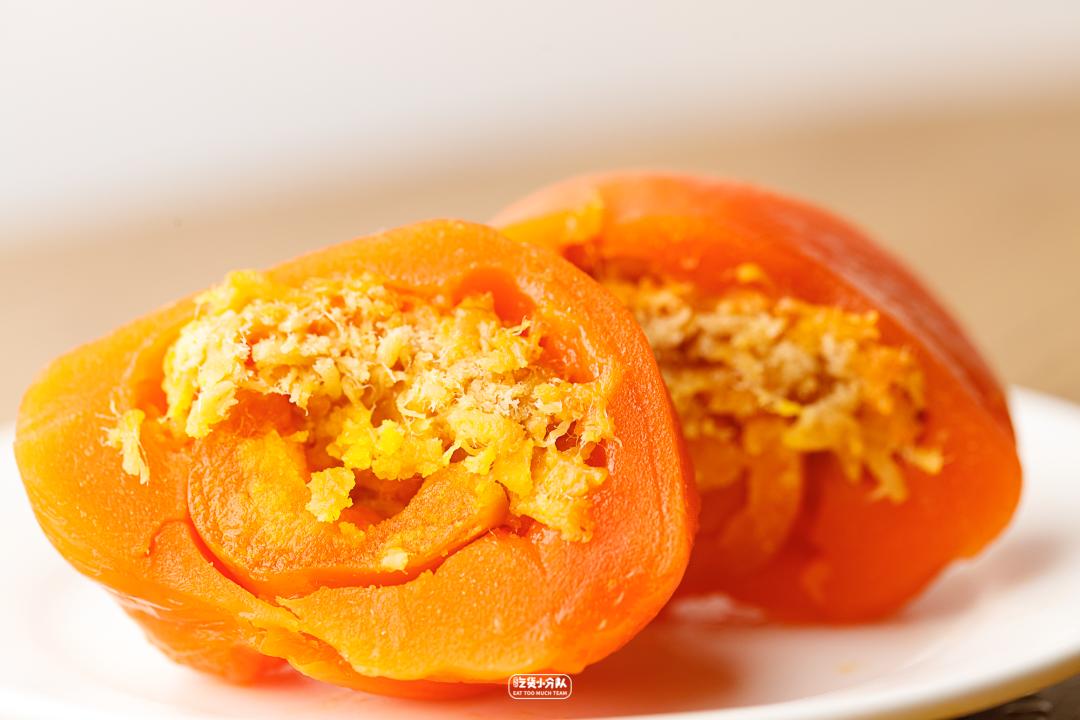
Wuxi food market online celebrity gaotuan

Xiao Hong Gao Tuan Branch (Daoxiang Branch) Egg Yolk Rousong
Skin look and feel: relatively large
Skin taste: fresh
Filling fullness: fullness
Overall sweetness: 4.5 points
Overall deliciousness: 8.5 points (only refers to purchasing)
Cost performance: 9 yuan/only.
takeaway
Taobao daigou
evaluate
The online celebrity cake group in Wuxi food market has been in operation for more than 20 years.
There are two municipal medals on the facade, so hot that there are scalpers and daigou.
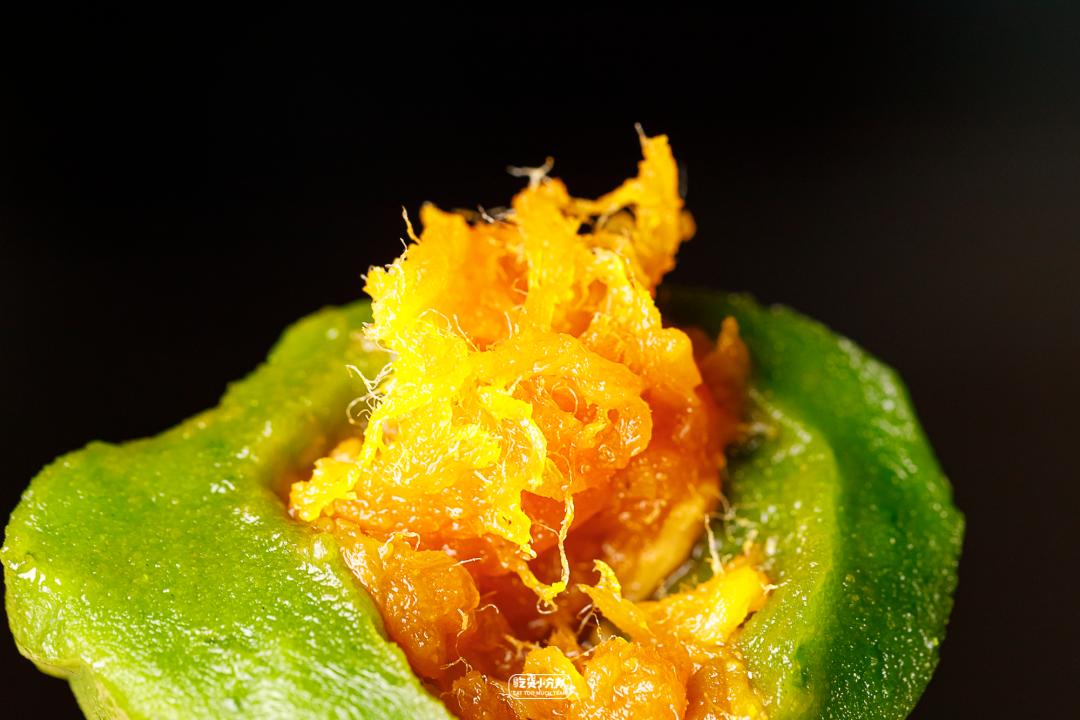

Maybe it took a whole day to transport it, but it was still frozen. When I got it, it was already hard. A lot of stuffing is given, and the outer skin is slightly thick to wrap the stuffing in the middle.
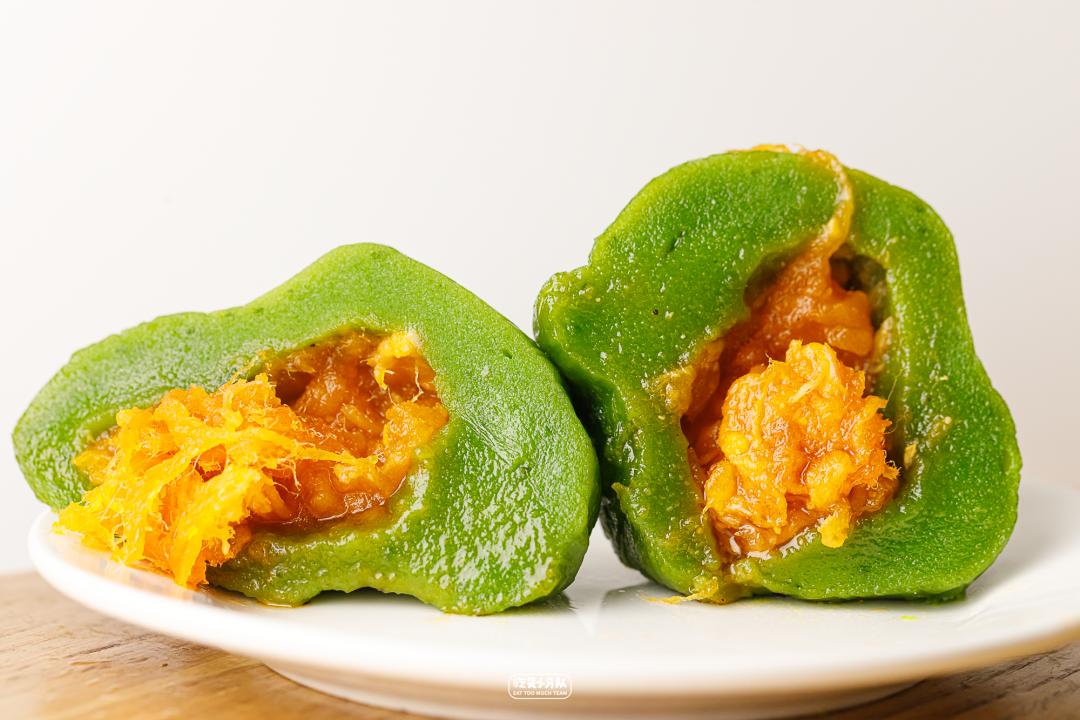

The stuffing in the middle is very delicious, with distinct threads, fresh and sweet taste, and the aroma of eggs will stay in the mouth for a long time. Even if there are many old brands in Shanghai, it is still the most fragrant salted egg yolk invaginated in this evaluation. I have been planted with grass, so I must eat it when I go to the local area!
2. Nanjing local manpower pushes the Youth League
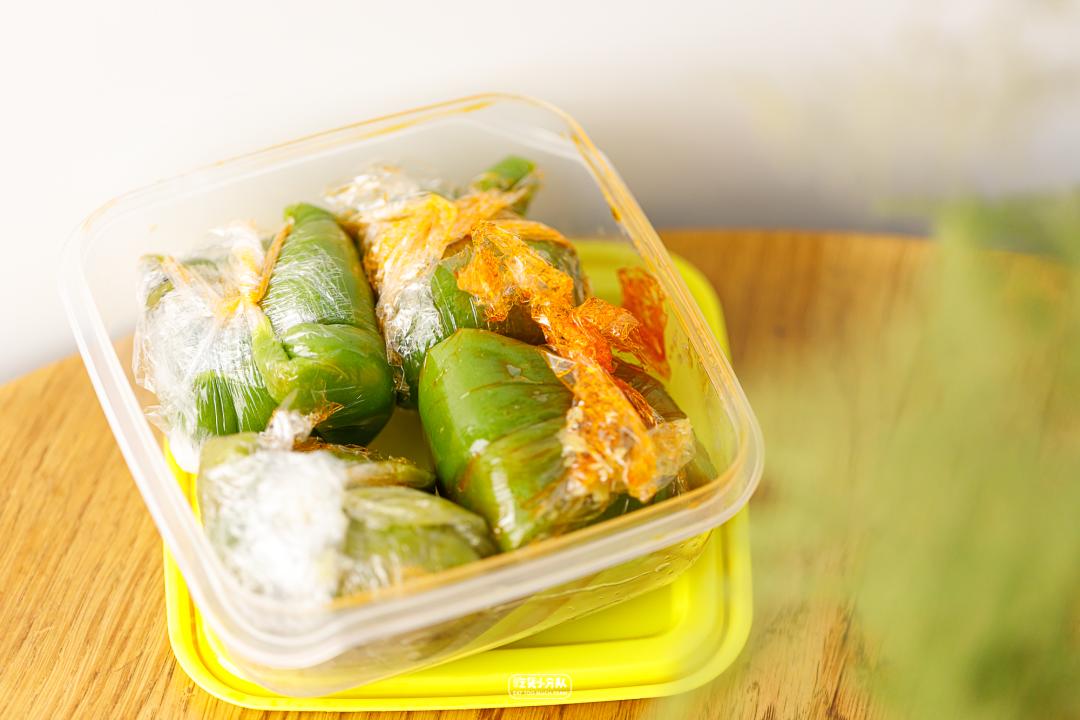

Xu Ayi Qingtuan Egg Yolk Rousong
Skin impression: each one is full and half the size of a fist.
Skin taste: fragrant and glutinous.
Filling fullness: full
Overall sweetness: 6 points
Overall deliciousness: 8 points (only refers to purchasing)
Cost performance: 8 yuan/only.
takeaway
Taobao daigou
* backstage reply keyword "Youth League" to see the full version.
evaluate
This is an old handmade shop pushed by local manpower in Nanjing.
Hidden in the alley, but still a long queue.
Ranked first in the Nanjing cake group heat list.
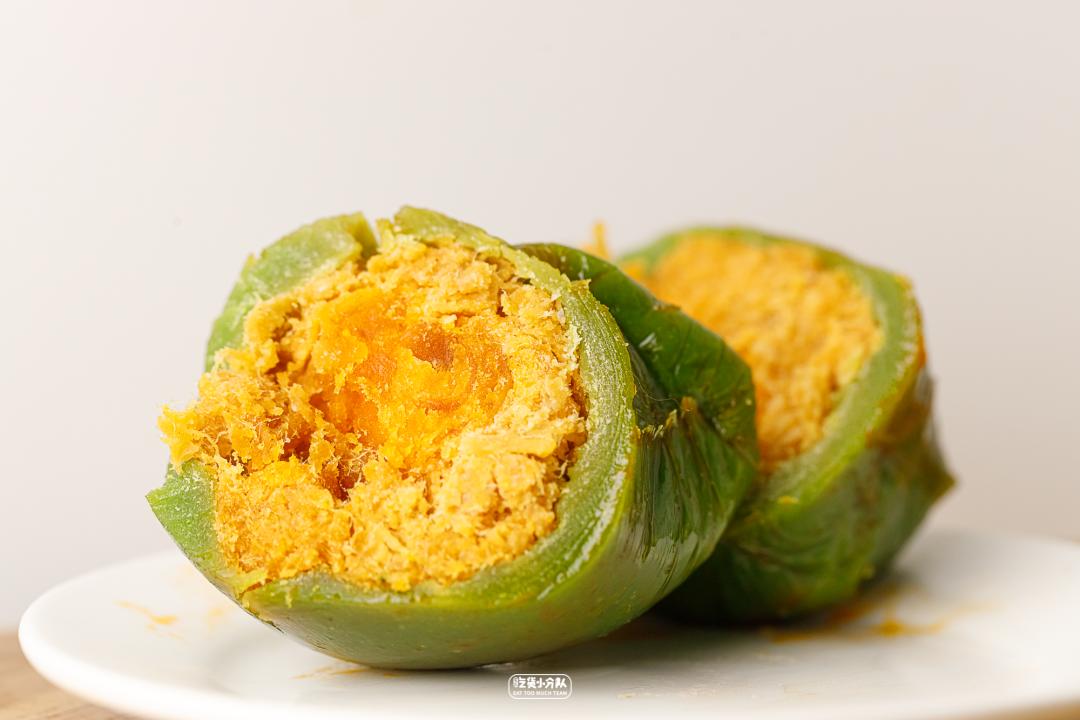

It looks full and round to the naked eye. When fresh, the smell of rice and wormwood is very strong. When heated, the room is full of fragrance. The egg yolk inside is a whole one, which is very fragrant.
3. Suzhou Net Red Auntie Youth League
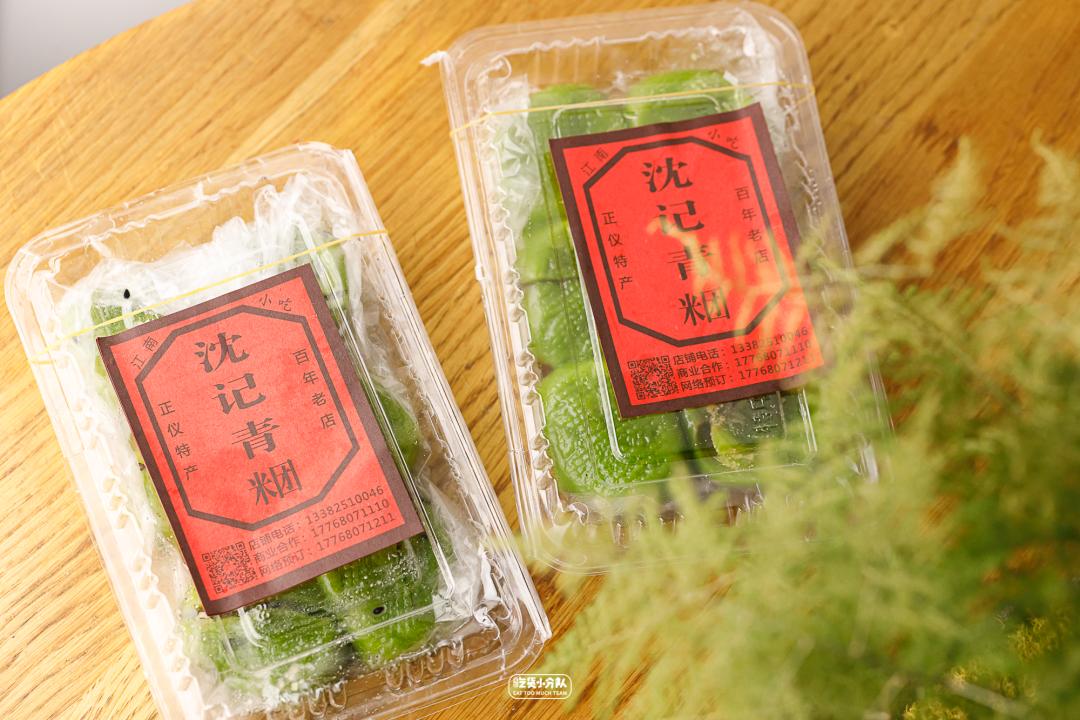

Suzhou Shen Ji Qing Tuan zhi ma dou sha
Skin impression: relatively small, 1 mouth, 1.
Filling fullness: fullness
Cost-effective ratio: 1 yuan with bean paste/1.5 yuan with sesame seeds/only.
takeaway
Taobao daigou
* backstage reply keyword "Youth League" to see the full version.
evaluate
Aunt Shen Jianfen, the proprietress, inherited her craft from her grandfather.
It has been made for decades and is the most popular cake group in Suzhou.
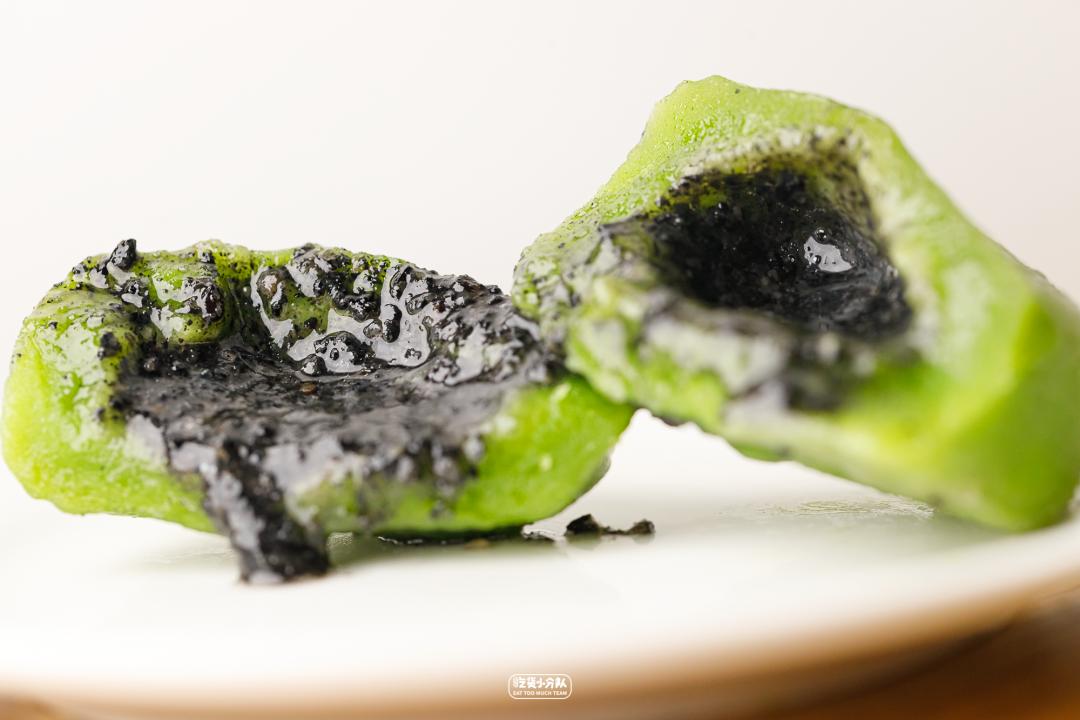


The youth league is the smallest in this evaluation, only 2-3 coins in size. But the cost performance is very high, with an average price of more than 1 yuan. Sesame stuffing is still flowing. In addition to the traditional tastes, there are also innovative new flavors such as chocolate stuffing, five kernels and hundred fruits.
●
VOL.04
Rollover group, but the cost performance is ok.
Maybe the greater the expectation, the more I want to spur.
For the sake of cost performance, comfort yourself, what kind of bike do you want?
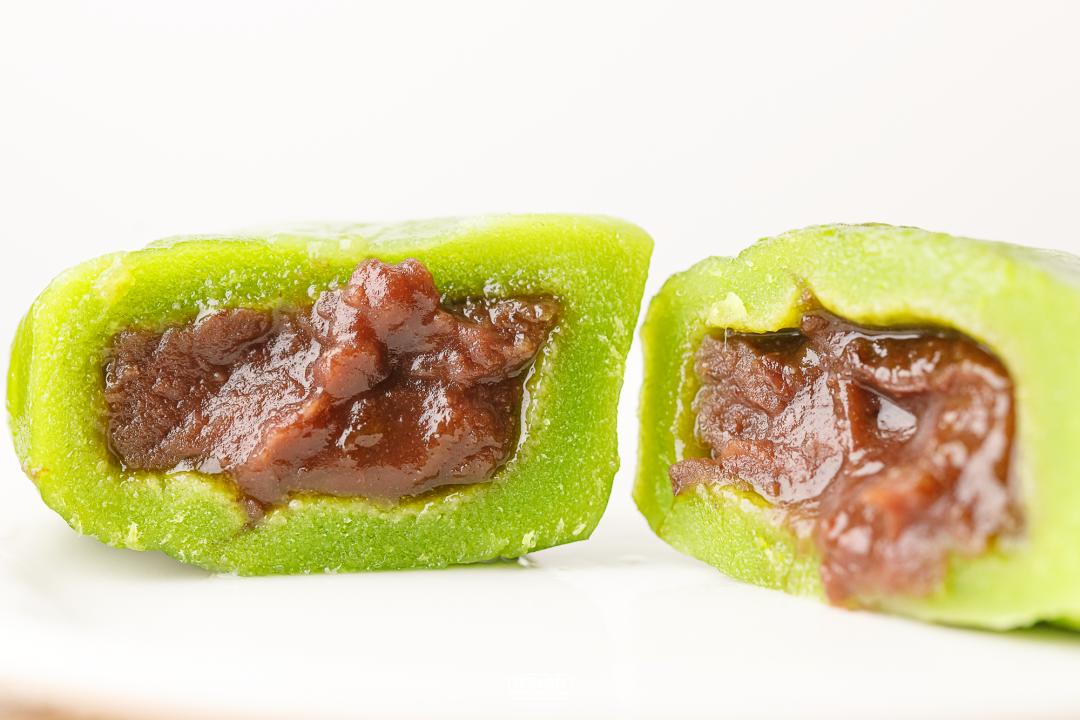
1. The green ball delayed by the skin

Master Bao’s egg yolk meat floss green ball
Skin impression: small one, good shape.
Skin taste: smells light aroma, slightly salty, Q-bomb.
Filling fullness: not bad
Overall sweetness: 7 points
Overall delicacy: 6.5 points
Cost performance: 22 yuan/box /4 PCs.
takeaway
Meituan (Quanchengsong)
* backstage reply keyword "Youth League" to see the full version.
evaluate
Master Bao, who is famous for his meat floss, made the meat floss into a green ball.
It’s a little overturned, but the price is cheap in the egg yolk meat floss youth group.

The invagination is a delicate meat floss, salty and fragrant. It may be because the invagination is rich, so it is matched with a thicker outer skin.

Whether the skin chews is soft or not, but the Q-bomb is brittle and tough. However, the skin is a little salty, and the sweet party is a little incompetent. It is better to eat the whole one together.
Summary of this evaluation
1. Eat Youth League. You can’t go wrong by picking one of the most recognized old brands in Shanghai.
2. Qing Tuan, freshly baked is the best, and it is best to eat it while it is hot.
3. online celebrity style, the leather is far less than the existing one, and there is much novelty in it.
3. The youth league from other places tends to beat the Shanghai Youth League, but no matter how delicious it is, the taste will be discounted after transportation, so you must go to the local area to eat.
Heating TIPS
1. It’s better to eat it while it’s fresh.
2. The microwave oven usually lasts for 30 seconds. If it is overheated, it will lose water and harden.
3. It usually takes a few minutes to steam over the water, and it is easy to steam the skin.
4. If you want to keep it for a long time, you can put it in the freezer and steam it when you eat it.
* The method of heating greatly affects the taste, otherwise the delicious green balls will be spoiled.
Keyword reply "Youth League"
View the full version of Shanghai Youth League takeaway list.
Including purchase channel+taste+where can I buy it?
Photography | Liu Chuanfeng Design | Lao Wang next door
* The pictures and words in the text are original by the team.
The thief is far away.

Takeaway list 1, Minhang article
Shanghai 2022 Online Shopping Raiders
After unsealing, eat all over Xuhui together.
"Being slightly fat is the best figure"
– The End –
Original title: "Evaluation of 78 Youth Groups, with a list of takeout in the whole city"
Read the original text